SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D. C. 20549
FORM 10-K
|
| | |
þ | | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| | For The Fiscal Year Ended June 29, 2013 |
o | | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission File No. 1-15583
DELTA APPAREL, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
| | |
Georgia (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | 58-2508794 (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
322 South Main Street
Greenville, SC 29601
(Address of principal executive offices) (zip code)
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (864) 232-5200
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
| | |
Title of Each Class | | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered |
Common Stock, par value $0.01 | | NYSE MKT LLC |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned filer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No þ.
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No þ.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes þ No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes þ No o.
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
|
| | | | | | |
Large accelerated filer o | | Accelerated filer þ | | Non-accelerated filer o | | Smaller reporting company o |
| | | | (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | | |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes o No þ.
As of December 29, 2012, the aggregate market share of the registrant’s voting stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant (based on the last sale price for such shares as quoted by the NYSE MKT (then NYSE Amex) was approximately $105.8 million.
The number of outstanding shares of the registrant’s Common Stock as of August 22, 2013 was 7,809,948.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE:
Certain information required in Part III of this Form 10-K shall be incorporated from the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A for the registrant’s 2013 Annual Meeting of Shareholders currently scheduled to be held on November 7, 2013.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
EX-10.1 | |
EX-21 | |
EX-23.1 | |
EX-31.1 | |
EX-31.2 | |
EX-32.1 | |
EX-32.2 | |
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward Looking Statements
The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 provides a safe harbor for forward-looking statements made by or on behalf of the Company. We may from time to time make written or oral statements that are “forward-looking,” including statements contained in this report and other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), in our press releases, in oral statements, and in other reports to our shareholders. All statements, other than statements of historical fact, which address activities, events or developments that we expect or anticipate will or may occur in the future are forward-looking statements. The words “estimate”, “project”, “forecast”, “anticipate”, “expect”, “intend”, “believe” and similar expressions, and discussions of strategy or intentions, are intended to identify forward-looking statements.
The forward-looking statements in this Annual Report are based on our expectations and are necessarily dependent upon assumptions, estimates and data that we believe are reasonable and accurate but may be incorrect, incomplete or imprecise. Forward-looking statements are also subject to a number of business risks and uncertainties, any of which could cause actual results to differ materially from those set forth in or implied by the forward-looking statements. The risks and uncertainties include, among others:
| |
• | the volatility and uncertainty of cotton and other raw material prices; |
| |
• | the general U.S. and international economic conditions; |
| |
• | deterioration in the financial condition of our customers and suppliers and changes in the operations and strategies of our customers and suppliers; |
| |
• | the competitive conditions in the apparel and textile industries; |
| |
• | our ability to predict or react to changing consumer preferences or trends; |
| |
• | pricing pressures and the implementation of cost reduction strategies; |
| |
• | changes in the economic, political and social stability of our offshore locations; |
| |
• | our ability to retain key management; |
| |
• | the effect of unseasonable weather conditions on purchases of our products; |
| |
• | significant changes in our effective tax rate; |
| |
• | any restrictions on our ability to borrow capital or service our indebtedness; |
| |
• | interest rate fluctuations increasing our obligations under our variable rate indebtedness; |
| |
• | the ability to raise additional capital; |
| |
• | the ability to grow, achieve synergies and realize the expected profitability of recent acquisitions; |
| |
• | the volatility and uncertainty of energy and fuel prices; |
| |
• | any material disruptions in our information systems related to our business operations; |
| |
• | any data security or privacy breaches; |
| |
• | any significant interruptions within our distribution network; |
| |
• | changes in or our ability to comply with safety, health and environmental regulations; |
| |
• | any significant litigation in either domestic or international jurisdictions; |
| |
• | the ability to protect our trademarks and other intellectual property; |
| |
• | the ability to obtain and renew our significant license agreements; |
| |
• | the impairment of acquired intangible assets; |
| |
• | changes in e-commerce laws and regulations; |
| |
• | changes to international trade regulations; |
| |
• | changes in employment laws or regulations or our relationship with our employees; |
| |
• | cost increases and reduction in future profitability due to recent healthcare legislation; |
| |
• | foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations; |
| |
• | violations of manufacturing or employee safety standards, labor laws, or unethical business practices by our suppliers and independent contractors; |
| |
• | the illiquidity of our shares; |
| |
• | price volatility in our shares and the general volatility of the stock market; and |
| |
• | the costs required to comply with the regulatory landscape regarding public company governance and disclosure. |
A detailed discussion of significant risk factors that have the potential to cause actual results to differ materially from our expectations is described in Part 1 under the heading of “Risk Factors.” Accordingly, any forward-looking statements do not purport to be predictions of future events or circumstances and may not be realized. We do not undertake publicly to update or revise the forward-looking statements even if it becomes clear that any projected results will not be realized.
PART I
“Delta Apparel”, the “Company”, “we”, “us” and “our” are used interchangeably to refer to Delta Apparel, Inc. together with our domestic wholly-owned subsidiaries, including M.J. Soffe, LLC (“Soffe”), Junkfood Clothing Company (“Junkfood”), To The Game, LLC (“To The Game”), Art Gun, LLC (“Art Gun”), and other international subsidiaries, as appropriate to the context.
We were incorporated in Georgia in 1999 and our headquarters is located at 322 South Main Street, Greenville, South Carolina 29601 (telephone number: 864-232-5200). Our common stock trades on the NYSE MKT under the symbol “DLA”.
We operate on a 52-53 week fiscal year ending on the Saturday closest to June 30. The 2013, 2012 and 2011 fiscal years were 52-week years and ended on June 29, 2013, June 30, 2012 and July 2, 2011, respectively.
OVERVIEW
Delta Apparel, Inc. is an international apparel design, marketing, manufacturing and sourcing company that features a diverse portfolio of lifestyle basics and branded activewear apparel and headwear. We specialize in selling casual and athletic products through a variety of distribution channels and distribution tiers, including specialty stores, boutiques, department stores, mid and mass channels, college bookstores and the U.S. military. Our products are made available direct-to-consumer on our websites at www.soffe.com, www.junkfoodclothing.com, www.saltlife.com and www.deltaapparel.com. We believe this diversified distribution allows us to capitalize on our strengths to provide casual activewear and headwear to consumers purchasing from most types of retailers.
We design and internally manufacture the majority of our products, which allows us to offer a high degree of consistency and quality controls as well as leverage scale efficiencies. One of our strengths is the speed with which we can reach the market from design to delivery. We have manufacturing operations located in the United States, El Salvador, Honduras and Mexico, and use domestic and foreign contractors as additional sources of production. Our distribution facilities are strategically located throughout the United States to better serve our customers with same-day shipping on our catalog products and weekly replenishments to retailers.
ACQUISITIONS
We became a diversified branded apparel company through seven acquisitions which we have completed since October 2003. These acquisitions added well-recognized brands and licensed properties to our portfolio, expanded our product offerings and broadened our distribution channels and customer base.
|
| | | | |
Business | | Date of Acquisition | | Business Segment |
The Cotton Exchange | | July 12, 2010 | | Branded |
Art Gun | | December 28, 2009 | | Branded |
To The Game | | March 29, 2009 | | Branded |
FunTees | | October 2, 2006 | | Basics |
Intensity Athletics | | October 3, 2005 | | Branded |
Junkfood Clothing | | August 22, 2005 | | Branded |
M.J. Soffe | | October 3, 2003 | | Branded |
BUSINESS SEGMENTS
We operate our business in two distinct segments: branded and basics. Although the two segments are similar in their production processes and regulatory environments, they are distinct in their economic characteristics, products, marketing and distribution methods.
The branded segment is comprised of our business units which are focused on specialized apparel garments and headwear to meet consumer preferences and fashion trends, and includes Soffe, Junkfood, To The Game and Art Gun. These branded embellished and unembellished products are sold through specialty and boutique shops, upscale and traditional department stores, mid-tier retailers, sporting goods stores, college bookstores and the U.S. military. Products in this segment are marketed under our lifestyle brands of Soffe®, Intensity Athletics®, Junk Food®, The Game®, American Threads™, Salt Life® and Realtree Outfitters® as well as other labels. The results of The Cotton Exchange have been included in the branded segment since its acquisition on July 12, 2010.
The basics segment is comprised of our business units primarily focused on garment styles that are characterized by low fashion risk, and includes our Delta Catalog and FunTees businesses. We market, distribute and manufacture for sale unembellished knit apparel under the main brands of Delta Pro Weight® and Delta Magnum Weight® for sale to a diversified audience ranging from large licensed screen printers to small independent businesses. We also manufacture private label products for major branded sportswear companies, retailers, corporate industry programs, and sports licensed apparel marketers. Typically these products are sold with value-added services such as hangtags, ticketing, hangers, and embellishment so that they are fully ready for retail.
See Note 13 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for financial information regarding segment reporting, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
PRODUCTS
We specialize in the design, merchandising, sales, and marketing of a variety of casual and athletic products for men, women, juniors, youth and children at a wide range of price points through most distribution channels.
We market fashion apparel garments and headwear under our primary brands of Soffe®, Intensity Athletics®, Junk Food®, and The Game®, as well as other labels. We market our basic apparel garments under our Delta brand.
Soffe is positioned in the marketplace as an All-American lifestyle active wear company that designs, produces, and markets product for men, women, and children. The women's offerings are rooted in our cheer heritage and include a performance segment that utilizes technical fabrics as well as crossover fun fashion apparel. The Soffe signature junior fit reigns supreme with our consumer base. As a supplier to the military since 1946, the men's offerings are rooted in our military heritage. The XT46 collection leverages performance fabrics and channels the military's authenticity with an emphasis on the soldier, the original elite athlete. We also support the on-the-field female athlete under Intensity Athletics. Intensity Athletics incorporates fashion on the field and trend leading fits to create uniforms, practice gear, and accessories.
Junk Food emerged in 1998 as the original vintage t-shirt company, creating and forever changing the premium t-shirt market. Known for its soft, comfortable fabrics and witty art, Junk Food is a celebrity favorite carried in the top stores throughout the world, including branded collaborations with Vans, Uniqlo and Gap Inc. Also a licensing powerhouse, Junk Food has distribution rights to over 800 pop-culture properties across multiple categories including rock & roll, iconic fictional characters, movies, sports, and foods and beverages. The brand continues to pave the way for innovation in the fashion industry. From recently launching their first retail stores as QR code walls in Westfield Malls to creating the first ever t-shirt allowing consumers to register to vote by scanning the graphic with their smartphones, Junk Food is revolutionizing the use of technology in fashion and culture. The company's diversified business model includes both private and branded labels, with a portfolio that includes Junk Food, Junk Food Art House, Worn Rite®, Paint + Cloth™, Stray Heart™, The Neighborhood Thieves®, Love + Art™, and True Vintage®.
The Game is an All-American sportswear and headwear company. Its innovative designs and superior quality products are sold nationally through sporting goods, college, outdoor, and specialty stores in addition to team dealers and online, where customers can create custom headwear designs. The Game has two signature headwear designs, “The Bar” and “The Circle” which are well recognized by consumers across the country. Worn by college athletes at over 1,000 colleges and universities, The Game is proud to be the headwear worn by many NCAA baseball and softball champions. The Game recently launched American Threads™, an American-made collegiate apparel and headwear collection. We are the exclusive licensee of Salt Life® apparel, headwear, footwear, decals, bags and other accessories, and hold an apparel license for Realtree Outfitters® and Realtree Girl® brands.
Art Gun provides customers with a virtual art studio to create customized graphics on apparel and other products. We are a leader in direct to garment printing and have one the most highly automated factory processes for delivering on-demand, direct to garment, digitally printed garments of all types, which we operate twenty four hours a day, seven days a week. We ship products to consumers in over 40 countries worldwide.
Delta offers more basic, high quality apparel garments for the entire family under its primary brand names Delta Pro Weight® and Delta Magnum Weight®. Delta products are offered in a wide range of colors available in six-month infant to adult sizes up to 4X. The Pro Weight® line represents a diverse selection of mid-weight, 100% cotton silhouettes in a large color palette. New in this mid-weight line is an adult tank offered in a variety of colors including trendy neon colors. The Magnum Weight® line is designed to give our customers a variety of silhouettes in a heavier-weight, 100% cotton fabric. New to the Delta line are the Delta-Dri™ performance t-shirts. This cotton/polyester blend product wicks moisture away from the skin and also includes an anti-microbial finish for odor control. Delta-Dri™ products are offered in long and short sleeves.
FunTees designs, markets and manufactures private label custom knit t-shirts primarily to major branded sportswear companies, including Nike, Quiksilver and Columbia Sportswear. The majority of this merchandise is embellished. Additionally, we offer our customers a wide variety of packaging services so the products can be shipped store-ready.
A key to our business success is our ability to anticipate and quickly respond to changing consumer preferences. We maintain a California-based design lab that provides trend reports, concepts and color trends to keep our products and designs in style. This information is used by our in-house designers and merchandisers, along with our sales and marketing personnel, who review market trends, sales results and the popularity of our latest products to design new merchandise to meet the expected future demands of our consumers.
TRADEMARKS AND LICENSE AGREEMENTS
We own several well-recognized trademarks that are important to our business. Soffe® has stood for quality and value in the athletic and activewear market for more than sixty years and Junk Food® has been known as a leading vintage t-shirt company since 1998. The Game® and Kudzu® have been registered trademarks since 1989 and 1995, respectively. Associated with The Game®, we also have registered trademarks for the Three-Bar-Design and the Circle Design, which are recognized collegiate designs. Other registered
trademarks include Delta®, American Threads™, The Cotton Exchange®, Quail Hollow®, and Intensity Athletics®. Our trademarks are valuable assets that differentiate the marketing of our products. We vigorously protect our trademarks and other intellectual property rights against infringement.
We have distribution rights to other trademarks through license agreements. The Soffe and The Game business units are official licensees for most major colleges and universities. Junkfood has rights to distribute trademarked apparel across athletics (including the NFL and NBA), music, entertainment, foods and beverages, and numerous other pop-culture categories. We also have license agreements for motorsports properties (including NASCAR), Churchill Downs, golf and other various resort properties. Our license agreements are typically non-exclusive in nature and have terms that range from one to three years. In addition, we are the exclusive licensee for t-shirts, fleece and headwear within the Realtree Outfitters® outdoor lifestyle apparel brand, and also a licensee for Realtree Girl® brand. We expanded our lifestyle brand apparel line in fiscal year 2011 by becoming the exclusive licensee for Salt Life® apparel, headwear, decals, bags and other accessories. In fiscal year 2012, we expanded our relationship with Salt Life® by becoming the exclusive licensee for footwear and also opened the flagship Salt Life® apparel retail store in Jacksonville Beach, Florida. While historically we have been able to renew our license agreements, the loss of certain license agreements could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations. Although we are not dependent on any single license, our license agreements collectively are of significant value to our branded segment.
SALES & MARKETING
Our sales and marketing function consists of both employed and independent sales representatives and agencies located throughout the country. In the branded segment, sales teams service specialty and boutique, upscale and traditional department stores, sporting goods, outdoor, military, and college bookstore customer bases. We also have a growing international presence with our Junk Food® products in Canada, Europe, Asia and Australia. In the basics segment, we sell our knit apparel products primarily direct to large and small screen printers and into the promotional products markets. Our private label products are sold primarily to major branded sportswear companies. Additionally, all brands leverage both in-house and outsourced marketing communications professionals to amplify their lifestyle statements.
During fiscal year 2013, we shipped our products to approximately 14,000 customers, many of whom have numerous retail "doors". No single customer accounted for more than 10% of sales in fiscal years 2013, 2012 or 2011, and our strategy is to not become dependent on any single customer. Revenues attributable to sales of our products in foreign countries represented approximately 2% of our total consolidated net sales in fiscal year 2013 and 1% of our total consolidated net sales in each of fiscal years 2012 and 2011.
The majority of our apparel products are produced based on forecasts to permit quick shipments to our customers. Private label programs are generally made only to order or based on a customer's forecast. Our headwear products are primarily sourced based on customer orders; however, we carry certain styles in inventory to support quick-turn shipments. We aggressively explore new ways to leverage our strengths and efficiencies to meet the quick-turn needs of our customers.
We have distribution facilities strategically located throughout the United States that carry in-stock inventory for shipment to customers, with most shipments made via third party carriers. In order to better serve customers, we allow products to be ordered by the piece, dozen, or full case quantities. Because a significant portion of our business consists of at-once replenishment and direct catalog orders, we believe that backlog order levels do not provide a general indication of future sales.
COMPETITION
We have numerous competitors with respect to the sale of apparel and headwear products in domestic and international markets, many of which have greater financial resources than we do.
We believe that competition within our branded segment is based primarily upon design, brand recognition, and consumer preference. We focus on sustaining the strong reputation of our brands by adapting our product offerings to changes in fashion trends and consumer preferences. We keep our merchandise fresh with unique artwork and new designs, and support the integrated lifestyle statement of our products through effective consumer marketing. We believe that our favorable competitive position stems from strong consumer recognition and brand loyalty, the high quality of our products, and our flexibility and process control, which drive product consistency. Our ability to remain competitive in the areas of quality, price, design, marketing, product development, manufacturing, technology and distribution will, in large part, determine our future success.
Competition in our undecorated basics business is generally based upon price, service, delivery time and quality, with the relative importance of each factor depending upon the needs of the particular customers and the specific product offering. This business is highly price competitive and competitor actions can greatly influence pricing and demand for our products. While price is still important in the private label market, quality and service are more important factors for customer choice. Our ability to consistently service the needs of our private label customers greatly impacts future business with these customers.
SEASONALITY
Although our various product lines are sold on a year-round basis, the demand for specific products or styles reflects some seasonality, with sales in our fourth fiscal quarter typically being the highest and sales in our second fiscal quarter typically being the lowest. As we
continue to expand our product offerings, the seasonality in our business has become less pronounced. The percentage of net sales by quarter for the year ended June 29, 2013, was 27%, 22%, 24% and 27% for the first, second, third, and fourth fiscal quarters, respectively. Consumer demand for apparel is largely influenced by the overall U.S. economy and consumer spending in general. Therefore, the distribution of sales by quarter in fiscal year 2013 may not be indicative of the distribution in future years.
MANUFACTURING
We have a vertically integrated manufacturing platform that supports both our branded and basics segments. Our manufacturing operations begin with the purchase of yarn and other raw materials from third-party suppliers. We manufacture fabrics in either our owned domestic textile facility located in Maiden, North Carolina or at Ceiba Textiles, our leased textile facility located near San Pedro Sula, Honduras. The manufacturing process continues at one of our seven apparel manufacturing facilities where the products are ultimately sewn into finished garments. We either own these facilities or lease and operate them. These facilities are located domestically (two in North Carolina) and internationally (two in Honduras, one in El Salvador and two in Mexico). Our garments may also be embellished and prepared for retail sale (with any combination of services, including ticketing, hang tags, and hangers). These facilities are located domestically (one in Alabama and one in North Carolina) and internationally (one in El Salvador and one in Mexico). In fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011, approximately 81%, 73% and 69%, respectively, of our manufactured products were sewn in company-operated locations. The remaining products were sewn by outside contractors located primarily in the Caribbean Basin.
At the 2013, 2012 and 2011 fiscal year-ends, our long-lived assets in Honduras, El Salvador and Mexico collectively comprised approximately 42%, 44% and 45%, respectively, of our total net property, plant and equipment, with our long-lived assets in Honduras comprising 31%, 34% and 37%, respectively. See Item 1A. Risk Factors for a description of risks associated with our operations located outside of the United States.
To supplement our internal manufacturing platform, we purchase fabric, undecorated products and full-package products from independent sources throughout the world. In fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011, we sourced approximately 19%, 20% and 23%, respectively, of our products from third parties.
RAW MATERIALS
We have a supply agreement with Parkdale Mills, Inc. and Parkdale America, LLC (collectively"Parkdale") to supply our yarn requirements until December 31, 2015. Under the supply agreement, we purchase from Parkdale all of our yarn requirements for use in our manufacturing operations, excluding yarns that Parkdale does not manufacture or cannot manufacture due to temporary capacity constraints. The purchase price of yarn is based upon the cost of cotton plus a fixed conversion cost. If Parkdale’s operations are disrupted and it is not able to provide us with our yarn requirements, we may need to obtain yarn from alternative sources. Although alternative sources are presently available, we may not be able to enter into short-term arrangements with substitute suppliers on terms as favorable as our current terms with Parkdale. In addition, the cotton futures we have fixed with Parkdale may not be transferable to alternative yarn suppliers. Because there can be no assurance that we would be able to pass along the higher cost of yarn to our customers, this could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations. During calendar year 2011, the apparel industry as a whole experienced unprecedented increases in cotton prices leading to ensuing price volatility in calendar 2012. The record high cotton prices, coupled with price discounting that occurred in the basic, undecorated t-shirt market, led to our decision to take a $16.2 million inventory writedown in our basics segment in the second fiscal quarter of 2012, which was the primary factor in the Company's net loss for fiscal year 2012.
We also purchase specialized fabrics that we currently do not have the capacity or capability to produce and may purchase other fabrics when it is cost-effective to do so. While these fabrics typically are available from various suppliers, there are times when certain yarns become limited in quantity, causing some fabrics to be difficult to source. This can result in higher prices or the inability to provide products to customers, which could negatively impact our results of operations. Dyes and chemicals are also purchased from several third party suppliers. While historically we have not had difficulty obtaining sufficient quantities of dyes and chemicals for manufacturing, the availability of products can change, which could require us to adjust dye and chemical formulations. In certain instances, these adjustments can increase manufacturing costs, negatively impacting our results of operations.
EMPLOYEES AND SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
As of June 29, 2013, we employed approximately 7,000 full time employees, of whom approximately 1,600 were employed in the United States. There are approximately 1,000 employees at one of our facilities in San Pedro Sula, Honduras covered by a collective bargaining agreement. In 2012 we received notice from the Honduran Labor Ministry that a petition for union representation of employees at a separate facility in San Pedro Sula, Honduras had been filed. We have since entered into the collective bargaining process in connection with this petition. We have historically conducted our operations without significant labor disruptions and believe that our relations with our employees are good. We have invested significant time and resources in ensuring that the working conditions in all of our facilities meet or exceed the standards imposed by the governing laws and regulations. We have obtained WRAP (Worldwide Responsible Accredited Production) certification for all of our manufacturing facilities that we operate in the United States, Honduras, El Salvador and Mexico. In 2011 Delta Apparel, Inc., along with all of its affiliated businesses, became a participating company of the FLA (Fair Labor Association). This affiliation with FLA further enhances human rights compliance monitoring for our plants and our third party
contractors. In addition, we have proactive programs to promote workplace safety, personal health, and employee wellness. We also support educational institutions and charitable organizations in the communities where we operate.
ENVIRONMENTAL AND REGULATORY MATTERS
We are subject to various federal, state and local environmental laws and regulations concerning, among other things, wastewater discharges, storm water flows, air emissions and solid waste disposal. Our plants generate very small quantities of hazardous waste, which are either recycled or disposed of off-site. Most of our plants are required to possess one or more environmental permits, and we believe that we are currently in compliance with the requirements of these permits.
The environmental regulations applicable to our business are becoming increasingly stringent and we incur capital and other expenditures annually to achieve compliance with environmental standards. We currently do not expect that the amount of expenditures required to comply with these environmental standards will have a material adverse effect on our operations, financial condition or liquidity. There can be no assurance, however, that future changes in federal, state, or local regulations, interpretations of existing regulations or the discovery of currently unknown problems or conditions will not require substantial additional expenditures. Similarly, while we believe that we are currently in compliance with all applicable environmental requirements, the extent of our liability, if any, for past failures to comply with laws, regulations and permits applicable to our operations cannot be determined and could have a material adverse effect on our operations, financial condition and liquidity.
RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT
Although we continually seek new products and brands to take to market via our diverse distribution network and customer base, there were no material amounts expended on research and development in the fiscal year ended June 29, 2013.
AVAILABLE INFORMATION
Our corporate internet address is www.deltaapparelinc.com. We make available free of charge on our website our SEC reports, including our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, Section 16 filings and any amendments to those reports, as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the SEC. The information found on our website is not part of this, or any other, report that we file with or furnish to the SEC.
In addition, we will provide upon request, at no cost, paper or electronic copies of our reports and other filings made with the SEC. Requests should be directed to: Investor Relations Department, Delta Apparel, Inc., 322 South Main Street, Greenville, South Carolina 29601. Requests can also be made by telephone to 864-232-5200 extension 6621, or via email at investor.relations@deltaapparel.com.
We operate in a rapidly changing, highly competitive business environment that involves substantial risks and uncertainties, including, but not limited to, the risks identified below. The following factors, as well as factors described elsewhere in this report or in our other filings with the SEC, which could materially affect our business, financial condition or operating results and the value of Company securities held by investors, should be carefully considered in evaluating our Company and the forward-looking statements contained in this report or future reports. The risks described below are not the only risks facing Delta Apparel. Additional risks not presently known to us or that we currently do not view as material, may become material, and may impair our business operations. Any of these risks could cause, or contribute to causing, our actual results to differ materially from expectations. We expressly disclaim any obligation to publicly update or revise any risk factors, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law.
The price and availability of purchased yarn and other raw materials is prone to significant fluctuations and volatility. Cotton is the primary raw material used in the manufacture of our apparel products. The price of cotton fluctuates and is affected by weather, consumer demand, speculation on the commodities market, and other factors that are generally unpredictable and beyond our control. As described under the heading “Raw Materials”, the price of yarn purchased from Parkdale, our key supplier, is based upon the cost of cotton plus a fixed conversion cost. We set future cotton prices with purchase commitments as a component of the purchase price of yarn in advance of the shipment of finished yarn from Parkdale. Prices are set according to prevailing prices, as reported by the New York Cotton Exchange, at the time we enter into the commitments. Thus, we are subject to the commodity risk of cotton prices and cotton price movements, which could result in unfavorable yarn pricing for us. In addition, if Parkdale’s operations are disrupted and it is not able to provide us with our yarn requirements, we may need to obtain yarn from alternative sources. We may not be able to enter into short-term arrangements with substitute suppliers on terms as favorable as our current terms with Parkdale, which could negatively affect our business. The Company and the apparel industry as a whole experienced unprecedented increases in cotton prices and price volatility during the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012. We were unable to pass through to our customers this higher cost cotton and ultimately decided to take a $16.2 million inventory writedown in our basics segment in the second quarter of our 2012 fiscal year. This second quarter inventory writedown was the primary factor in the Company's net loss for fiscal year 2012.
Current economic conditions may adversely impact demand for our products. The apparel industry is cyclical and dependent upon the overall level of discretionary consumer spending, which changes as regional, domestic and international economic conditions change. These economic conditions include, but are not limited to, employment levels, energy costs, interest rates, tax rates, inflation, personal
debt levels, and uncertainty about the future, with many of these factors outside of our control. Overall, consumer purchases of discretionary items tend to decline during recessionary periods when disposable income is lower. As such, deterioration in general economic conditions that creates uncertainty or alters discretionary consumer spending habits could reduce our sales. Because we match our manufacturing production to demand, weakening sales may require us to reduce output, thereby increasing per unit costs and lowering our gross margins, causing a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Deterioration in the financial condition of our customers or suppliers and changes in the operations and strategies of our customers or suppliers could adversely affect our financial position and results of operations. We extend credit to our customers, generally without requiring collateral. The extension of credit involves considerable judgment and is based on an evaluation of each customer’s financial condition and payment history. We monitor credit risk exposure by periodically obtaining credit reports and updated financial statements on our customers. Deterioration in the economy, declines in consumer purchases of apparel, or disruption in the ability of our customers to access liquidity could have an adverse effect on the financial condition of our customers. During the past several years, various retailers and other customers have experienced significant difficulties, including restructurings, bankruptcies and liquidations. The inability of these retailers and other customers to overcome these difficulties may increase due to the current worldwide economic conditions. We maintain an allowance for doubtful accounts for potential credit losses based upon current conditions, historical trends and other available information. However, the inability to collect on sales to significant customers or a group of customers could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. Significant changes in the financial condition of any of our suppliers or other parties with which we do business could result in disruption to our business and have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, significant changes in the retail or operational strategies employed by our customers may result in decreased sales of our products to such customers and could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. Likewise, significant changes in the operations of any of our suppliers or other parties with which we do business could result in disruption to our business and have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
The apparel industry is highly competitive, and we face significant competitive threats to our business. The market for athletic and activewear apparel and headwear is highly competitive and includes many new competitors as well as increased competition from established companies, some of which are larger, more diversified, and may have greater financial resources than we do. Many of our competitors have competitive advantages, including larger sales forces, better brand recognition among consumers, larger advertising budgets, and greater economies of scale. If we are unable to compete successfully with our competitors, our business and results of operations will be adversely affected.
Our success depends, in part, on our ability to predict or effectively react to changing consumer preferences and trends. The success of our businesses depends on our ability to anticipate and respond quickly to changing consumer demand and preferences in apparel and headwear. We believe that our brands are recognized by consumers across many demographics. The popularity, supply and demand for particular products can change significantly from year to year based on prevailing fashion trends and other factors and, accordingly, our ability to adapt to fashion trends in designing products is important to the success of our brands. If we are unable to quickly adapt to changes in consumer preferences in the design of products, our results of operations could be adversely affected.
Our basics segment is subject to significant pricing pressures which may decrease our gross profit margins if we are unable to implement our cost reduction strategies. We operate our basics segment in a highly competitive, price sensitive industry. Our strategy in this market environment is to be a low-cost producer and to differentiate ourselves by providing quality products and value-added services to our customers. To help achieve this goal, we began production in Ceiba Textiles, our Honduran textile facility, in fiscal year 2008. In the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2009, we closed our Soffe textile manufacturing facility in Fayetteville, North Carolina and moved this production to our Maiden, North Carolina and Ceiba Textiles plants. In fiscal year 2010, we began the expansion of Ceiba Textiles to increase internal manufacturing capacity and further leverage the fixed cost of the facility, and continued the expansion during fiscal year 2011. In fiscal year 2012, we moved several functions of our private label business to our El Salvador facility to better serve customers through an enhanced and efficient product development process. In conjunction with this, we began a modernization of our decoration equipment to expand capabilities and lower costs. In addition, we recently announced the consolidation of our domestic screen print operations as part of our continued focus on more efficient manufacturing and distribution strategies. This consolidation results in the closing of the Wendell, North Carolina decoration facility operated by our Soffe business unit and the consolidation of those operations within Soffe's Fayetteville, North Carolina facility. See Note 17 - Subsequent Events to the Consolidated Financial Statements. These initiatives, along with continual improvements in our production and delivery of products, are expected to lower our product costs and improve our results of operations. However, any unexpected increases in the costs to carry out these initiatives or the failure to achieve the cost savings expected from these initiatives could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Our operations are subject to political, social, economic, and climate risks in Mexico, Honduras and El Salvador. The majority of our products are manufactured in Honduras, El Salvador and Mexico, with a concentration in Honduras. These countries have experienced political, social and economic instability in the past, and we cannot be certain of their future stability. Instability in a country can lead to protests, riots and labor unrest. New government leaders can change employment laws, thereby increasing our costs to operate in that country. In addition, fire or natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, or floods can occur in these countries. Any of these political, social, economic or climatic events or conditions could disrupt our supply chain or increase our costs, adversely affecting our financial position and results of operations.
Our success depends upon the talents and continued contributions of our key management. We believe our future success depends on our ability to retain and motivate our key management, our ability to attract and integrate new members of management into our operations and the ability of all personnel to work together effectively as a team. Our continued success is dependent on our ability to retain existing, and attract additional, qualified personnel to execute our business strategy.
Our business is influenced by weather patterns. Our business is susceptible to unseasonable weather conditions. For example, extended periods of unusually warm temperatures during the winter season or cooler weather during the spring and summer seasons could render portions of our inventory incompatible with weather conditions and influence consumers to alter their apparel purchasing habits. Reduced sales volumes from extreme or prolonged unseasonable weather conditions could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
We currently pay income taxes at lower than statutory rates and may incur additional tax liability. We are subject to income tax in the United States and in foreign jurisdictions in which we generate net operating profits. We benefit from a lower overall effective income tax rate due to the majority of our manufacturing operations being located in foreign tax-free locations. Our U.S. legal entity contracts with our foreign subsidiaries to manufacture products on its behalf with the intercompany prices paid for the manufacturing services and manufactured products based on an arms-length standard and supported by an economic study. We have concluded that the profits earned in the tax-free locations will be considered permanently reinvested. Thus, no U.S. deferred tax liability is recorded on these profits, causing our effective tax rate to be significantly below U.S. statutory rates. Our effective tax rate could be adversely affected by changes in the mix of earnings between the U.S. and tax-free foreign jurisdictions. In addition, changes to U.S. tax laws impacting how U.S. multinational corporations are taxed on foreign earnings or a need or requirement for us to remit tax-free earnings back to the U.S. could also have a material adverse effect on our tax expense and cash flow.
We may be restricted in our ability to borrow under our revolving credit facility or service our indebtedness. Significant operating losses or significant uses of cash in our operations could cause us to default on our asset-based revolving credit facility. Our ability to borrow under the credit facility depends on our accounts receivable and inventory levels. A significant deterioration in our accounts receivable or inventory levels could restrict our ability to borrow funds or service our indebtedness. In addition, our credit facility includes a financial covenant that if the amount of availability falls below an amount equal to 12.5% of the lesser of the borrowing base or $145 million, our Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio (“FCCR”) (as defined in our credit agreement) for the preceding 12-month period must not be less than 1.1 to 1.0. In addition, the credit facility includes customary conditions to funding, representations and warranties, covenants, and events of default. The covenants include, among other things, limitations on asset sales, consolidations, mergers, liens, indebtedness, loans, investments, guaranties, acquisitions, dividends, stock repurchases, and transactions with affiliates. An event of default under the credit facility could result in an acceleration of our obligations under the agreement, in the foreclosure on any assets subject to liens in favor of the credit facility’s lenders, and in our inability to borrow additional amounts under the credit facility. Although our availability at June 29, 2013, was $42.0 million and our FCCR for the preceding twelve months was 2.0x, a significant decline in our profitability could cause our FCCR to fall below 1.1x, thereby requiring us to maintain a minimum availability as defined in our credit agreement. This action could restrict our ability to borrow funds or service our indebtedness and adversely affect our financial position and results of operations.
Our variable rate debt subjects us to interest rate risk that could cause our debt service obligations to increase significantly. The debt we incur under our asset-based revolving credit facility is at variable rates of interest, which exposes us to interest rate risk. If interest rates increase, our obligations on this variable rate indebtedness would increase even though the amount borrowed remained the same, and there would be a corresponding decrease in our net income and cash flows, including cash available for servicing our debt.
We may need to raise additional capital to grow our business. While our existing credit facility should be adequate to support our existing business in the foreseeable future, the rate of our growth, especially through acquisitions, will depend on the availability of debt and equity capital. We may not be able to raise capital on terms acceptable to us or at all. If new sources of financing are required, but are insufficient or unavailable, we may be required to modify our growth and operating plans based on available funding, which could adversely affect our ability to grow the business.
We have expanded our business through acquisitions that could result in diversion of resources, an inability to integrate acquired operations and extra expenses. A part of our growth strategy involves acquiring businesses that complement our existing business. The negotiation of potential acquisitions and integration of acquired businesses could divert our management’s attention from our existing businesses, which could negatively impact our results of operations. In addition, if the integration of an acquired business is not successful or takes significantly longer than expected, or if we are unable to realize the expected benefits from an acquired business, it could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
The price of energy and fuel costs are prone to significant fluctuations and volatility which could adversely affect our results of operations. Our manufacturing operations require high inputs of energy, and therefore changes in energy prices directly impact our gross profits. In addition, we incur significant freight costs to transport goods between the United States and our offshore facilities, along with transportation expenses to ship products to our customers. The cost of energy and fuel fluctuates due to a number of factors outside of our control, including government policy and regulation and weather conditions. We continue to focus on manufacturing methods that will reduce the amount of energy used in the production of products to mitigate risks of fluctuations in the cost of energy. In addition, we enter into forward contracts to fix a portion of the expected natural gas requirements for delivery in the future in order to mitigate
potential increases in costs. However, significant increases in energy and fuel prices may make us less competitive compared to others in the industry, which may have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Our business operations rely on our information systems and any material disruption or slowdown of our systems could cause operational delays. We depend on information systems to manage our inventory, process transactions, respond to customer inquiries, purchase, sell and ship goods on a timely basis and maintain cost-effective operations. We have invested significant capital and expect future capital expenditures associated with the integration of our information technology systems across our businesses. This process involves the replacement and consolidation of technology platforms so our businesses are served by fewer platforms, resulting in operational efficiencies and reduced costs. Our inability to effectively convert our operations to the new systems could cause delays in product fulfillment and reduced efficiency in our operations. In addition, we may experience operational problems with our information systems as a result of system failures, "cyber attack", computer viruses, security breaches, disasters or other causes. Any material disruption or slowdown of our information systems could cause operational delays that could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Data security and privacy breaches could lead to liability and reputational damage. Our business involves the regular collection and use of sensitive and confidential information regarding customers and employees. These activities are highly regulated and privacy and information security laws are complex and constantly changing. Compliance with these laws and regulations may result in additional costs due to new systems and processes and our non-compliance can lead to legal liability. Further, despite the security measures we have in place, any actual or perceived information security breach, whether due to "cyber attack", computer viruses or human error, could lead to damage to our reputation and a resulting material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our business could be harmed if we are unable to deliver our products to the market due to problems with our distribution network. We have owned and leased distribution facilities located throughout the United States. Any significant interruption in the operation of any of these facilities or our related sourcing and transportation logistics functions, whether within or outside of our control, may delay shipment of merchandise to our customers, potentially damaging our reputation and customer relationships and causing a loss of revenue. In addition, if we are unable to successfully coordinate the planning of inventory across these facilities and the distribution activities, it could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Failure of our operations to comply with safety, health and environmental regulations could have a material adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations. Our operations must meet extensive federal, state and local regulatory standards in the areas of safety, health and environmental pollution controls. There can be no assurance that interpretations of existing regulations, future changes in existing laws, or the enactment of new laws and regulations will not require substantial additional expenditures. Although we believe that we are in compliance in all material respects with existing regulatory requirements, the extent of our liability, if any, for the discovery of currently unknown problems or conditions, or past failures to comply with laws, regulations and permits applicable to our operations, cannot be determined and could have a material adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations.
We are subject to periodic litigation in both domestic and international jurisdictions that may adversely affect our financial position and results of operations. From time to time we may be involved in legal and regulatory actions regarding product liability, employment practices, intellectual property infringement, bankruptcies and other litigation. Due to the inherent uncertainties of litigation in both domestic and foreign jurisdictions, we cannot accurately predict the ultimate outcome of any such proceedings. These proceedings could cause us to incur costs and may require us to devote resources to defend against these claims and could ultimately result in a loss against these claims or other remedies such as product recalls, which could adversely affect our financial position and results of operations. For a description of current material legal proceedings, see Part I, Item 3, Legal Proceedings.
We rely on the strength of our trademarks and could incur significant costs to protect these trademarks and our other intellectual property. Our trademarks, including Soffe®, Junk Food®, and The Game® among others, are important to our marketing efforts and have substantial value. In addition, we have trademarked the Three-Bar-Design and the Circle Design, which are recognized collegiate designs. We aggressively protect these trademarks and have incurred legal costs in the past to establish and protect these trademarks, but these costs have not been significant. We may in the future be required to expend significant additional resources to protect these trademarks and our other intellectual property. The loss or limitation of the exclusive right to use our trademarks or other intellectual property could adversely affect our sales and results of operations.
A significant portion of our business relies upon license agreements. We rely on licensed products for a significant part of our sales. Although we are not dependent on any single license, we believe that our license agreements in the aggregate are of significant value to our business. The loss of or failure to obtain, renew or extend license agreements on favorable terms could adversely affect our sales and results of operations and have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
We may be subject to the impairment of acquired intangible assets. When we acquire a business, a portion of the purchase price of the acquisition may be allocated to goodwill and other identifiable intangible assets. The amount of the purchase price that is allocated to goodwill and other intangible assets is determined by the excess of the purchase price over the net identifiable assets acquired. At June 29, 2013, and June 30, 2012, our goodwill and other intangible assets were approximately $23.0 million and $23.6 million, respectively. We conduct an annual review, and more frequent reviews if events or circumstances dictate, to determine whether goodwill is impaired. We also determine whether impairment indicators are present related to our identifiable intangible assets. If we determine that goodwill or intangible assets are impaired, we would be required to write down the value of these assets. We completed our annual impairment
test of goodwill on the first day of our 2013 third fiscal quarter. Based on the valuation, there does not appear to be impairment on the goodwill associated with our Junkfood business unit, the only remaining goodwill recorded on our financial statements. We also concluded that there are no additional indicators of impairment related to our intangible assets. There can, however, be no assurance that we will not be required to take an impairment charge in the future, which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Changes in the regulations and laws regarding e-commerce could reduce the growth and lower the profitability of our internet sales. The e-commerce industry has undergone, and continues to undergo, rapid development and change. There have been continuing efforts to increase the legal and regulatory obligations and restrictions on companies conducting commerce through the internet, primarily in the areas of taxation, consumer privacy and protection of consumer personal information. These laws and regulations could increase the costs and liabilities associated with our e-commerce activities, thereby negatively impacting our results of operations.
Significant changes to international trade regulations could adversely affect our results of operations. The majority of our products are manufactured in Honduras, El Salvador and Mexico. We therefore benefit from current free trade agreements and other duty preference programs, including the North American Free Trade Agreement (“NAFTA”) and the Central America Free Trade Agreement (“CAFTA”). Our claims for duty free or reduced duty treatment under CAFTA, NAFTA and other available programs are largely conditioned on our ability to produce or obtain accurate records (some of which are provided to us by third parties) about production processes and sources of raw materials. Subsequent repeal or modification of NAFTA or CAFTA, or the inadequacy or unavailability of supporting records, could materially adversely affect our results of operations. In addition, our products are subject to foreign competition, which in the past has been faced with significant U.S. government import restrictions. The extent of import protection afforded to domestic apparel producers has been, and is likely to remain, subject to political considerations. The elimination of import protections for domestic apparel producers could significantly increase global competition, which could adversely affect our business.
Any failure to comply with international trade regulations could cause us to become subject to investigation resulting in significant penalties or claims or our inability to conduct business, adversely affecting our results of operations. A complaint was filed in March 2012 with the U.S. Department of Labor's Office of Trade & Labor Affairs by the AFL-CIO and various Honduran union federations alleging that the Honduran government failed to enforce its labor laws in violation of the provisions of CAFTA. The complaint contains various and sundry allegations of Honduran labor law violations by U.S.-based companies with Honduran operations, including our Ceiba Textiles operations. We contend that the allegations against Ceiba Textiles have no merit. The U.S. Department of Labor has initiated an investigation of the allegations in the complaint. The legal action, if any, that may result from this investigation would be an action by the U.S. government against Honduras under CAFTA, not a legal action against us related to the specific allegations contained in the complaint. However, an action against Honduras could result in sanctions or other penalties against Honduras under CAFTA or other governmental action that could have a material negative effect on our ability to conduct business there.
Changes in domestic or foreign employment regulations or changes in our relationship with our employees could adversely affect our results of operations. We employ approximately 7,000 employees worldwide, with approximately 5,400 of these employees being in Honduras, El Salvador or Mexico. Changes in domestic and foreign laws governing our relationships with our employees, including wage and human resources laws and regulations, fair labor standards, overtime pay, unemployment tax rates, workers' compensation rates and payroll taxes, would likely have a direct impact on our operating costs. A significant increase in wage rates in the countries in which we operate could have a material impact on our operating results. Our employees are currently not party to any collective bargaining agreements, with the exception of approximately 1,000 employees at one of our facilities in Honduras, which are party to a three-year collective bargaining agreement. In 2012 we received notice from the Honduran Labor Ministry that a petition for union representation of our employees at a separate facility in Honduras was filed and we have since entered into the collective bargaining process in connection with such petition. We have historically conducted our operations without significant labor disruptions and believe that our relations with our employees are good. However, if labor relations were to change, it could adversely affect the productivity and ultimate cost of our manufacturing operations.
Recent healthcare legislation may increase our costs and reduce our future profitability. To attract and retain employees, we maintain a competitive health insurance program for our employees and their dependents. The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, signed into law in 2010, is expected to increase our annual employee healthcare costs going forward. We cannot predict the effect that this legislation, or any future state or federal healthcare legislation or regulation, will have on our business. However, these rising healthcare costs and universal healthcare coverage in the United States could result in significant long-term costs to us, which could adversely affect our future profitability and financial condition. Also, rising healthcare costs could force us to make changes to our benefits program, which could negatively impact our ability to attract and retain employees.
We are subject to foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations. We manufacture the majority of our products outside of the United States, exposing us to currency exchange rate fluctuations. In addition, movements in foreign exchange rates can affect transaction costs because we source products from various countries. We may seek to mitigate our exposure to currency exchange rate fluctuations, but our efforts may not be successful. Accordingly, changes in the relative strength of the United States dollar against other currencies could adversely affect our business.
The value of our brands, sales of our products and our licensing relationships could be impacted by negative publicity resulting from violations of manufacturing or employee safety standards, labor laws, or unethical business practices by our suppliers and independent contractors. We are committed to ensuring that all of our manufacturing facilities comply with our strict internal code of
conduct, local and internal laws, and the codes and principles to which we subscribe, including those of the Worldwide Responsible Accredited Production (WRAP) and Fair Labor Association (FLA). In addition, we require our suppliers and independent contractors to operate their businesses in compliance with the laws and regulations that apply to them. However, we do not control these suppliers and independent contractors. A violation of our policies, applicable manufacturing or employee safety standards and codes of conduct, labor laws or other laws or regulations by our suppliers or independent contractors could interrupt or otherwise disrupt our operations. Negative publicity regarding the production methods of any of our suppliers or independent contractors or their failure to comply with our policies, applicable manufacturing or employee safety standards and codes of conduct, labor laws or other laws or regulations could adversely affect our reputation, brands, sales and licensing relationships, which could adversely affect our business.
The market price of our shares is affected by the illiquidity of our shares, which could lead to our shares trading at prices that are significantly lower than expected. Various investment banking firms have informed us that public companies with relatively small market capitalizations have difficulty generating institutional interest, research coverage or trading volume. This illiquidity can translate into price discounts as compared to industry peers or to the shares’ inherent value. We believe that the market perceives us to have a relatively small market capitalization. This could lead to our shares trading at prices that are significantly lower than our estimate of their inherent value.
As of August 22, 2013, we had 7,809,948 shares of common stock outstanding. We believe that approximately 61% of our stock is beneficially owned by entities and individuals who each own more than 5% of the outstanding shares of our common stock. Included in the 61% are institutional investors that beneficially own more than 5% of the outstanding shares. These institutional investors own approximately 49% of the outstanding shares of our common stock. Sales of substantial amounts of our common stock in the public market by any of these large holders could adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
The market price of our shares may be highly volatile and the stock market in general can be highly volatile. Fluctuations in Delta Apparel stock price may be influenced by, among other things, the general economic and market conditions, conditions or trends in our industry, changes in the market valuations of other apparel companies, announcements by us or our competitors of significant acquisitions, strategic partnerships or other strategic initiatives, and increased trading volumes. Many of these factors are beyond our control, but may cause the market price of our common stock to decline, regardless of our operating performance.
Efforts to comply with the evolving regulatory landscape regarding public company governance and disclosure will result in significant additional costs. We are committed to maintaining high standards for internal controls over financial reporting, corporate governance and public disclosure. However, evolving laws, regulations and standards relating to these issues such as the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, and similar regulations have created significant additional compliance requirements for companies like us. We have devoted and will continue to devote significant resources, and our management team has devoted and will continue to devote substantial time, to comply with these standards. This may lead to increases in our cost structure, divert the attention of our management team from revenue generating activities to compliance efforts, and could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
| |
ITEM 1B. | UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS |
None.
Our principal executive office is located in a leased facility in Greenville, South Carolina. We own and lease properties supporting our administrative, manufacturing, distribution and direct retail activities. Our products are manufactured through a combination of facilities that we either own, or lease and operate. As of June 29, 2013, we owned or leased twelve manufacturing facilities (located in the United States, Honduras, El Salvador and Mexico) and ten distribution facilities (all within the United States). In addition, we operated four leased factory-direct stores, one flagship retail store and maintained three leased showrooms.
Our primary manufacturing and distribution facilities are as follows:
|
| | | | |
Location | | Utilization | | Segment |
Maiden Plant, Maiden, NC | | Knit/dye/finish/cut | | Basics and branded |
Ceiba Textiles, Honduras* | | Knit/dye/finish/cut | | Basics and branded |
Honduras Plant, San Pedro Sula, Honduras* | | Sew | | Basics and branded |
Cortes Plant, San Pedro Sula, Honduras* | | Sew | | Basics and branded |
Mexico Plant, Campeche, Mexico* | | Cut/sew | | Basics and branded |
Textiles LaPaz, La Paz, El Salvador* | | Cut/sew/decoration | | Basics and branded |
Campeche Sportswear, Campeche, Mexico* | | Sew/decoration | | Basics and branded |
Fayetteville Plant, Fayetteville, NC | | Sew/decoration | | Branded |
Rowland Plant, Rowland, NC | | Sew | | Basics and branded |
Cotton Exchange, Wendell, NC* | | Decoration | | Branded |
Art Gun, Miami, FL* | | Decoration/distribution | | Branded |
Downing Drive, Phenix City, AL* | | Decoration/distribution | | Branded |
Warehouse, Louisville, KY* | | Distribution | | Branded |
Distribution Center, Clinton, TN | | Distribution | | Basics |
Distribution Center, Santa Fe Springs, CA* | | Distribution | | Basics and branded |
Distribution Center, Miami, FL* | | Distribution | | Basics and branded |
Distribution Center, Cranbury, NJ* | | Distribution | | Basics and branded |
DC Annex, Fayetteville, NC* | | Distribution | | Branded |
Distribution Center, Lansing, MI* | | Distribution | | Branded |
Distribution Center, Wendell, NC* | | Distribution | | Branded |
In fiscal year 2013, we began the expansion of our manufacturing capacity within our existing facilities to support the growth in our basics segment. This includes screen print modernization and expansion in both our international and U.S. facilities. We currently expect our facilities to run near full capacity during fiscal year 2014, but will take the necessary actions to balance capacities with demand as needed.We believe that all of our facilities are suitable for the purposes for which they are designed and are generally adequate to allow us to remain competitive. Substantially all of our assets are subject to liens in favor of our lenders under our U.S. asset-based secured credit facility and our Honduran loan.
U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission
We previously received an inquiry from the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (“Commission”) regarding a children's drawstring hoodie product sourced, distributed and sold by our Junkfood division and its compliance with applicable product safety standards. The Commission subsequently investigated the matter, including whether Junkfood complied with the reporting requirements of the Consumer Product Safety Act (“CPSA”), and the garments in question were ultimately recalled. On or about July 25, 2012, Junkfood received notification from the Commission staff alleging that Junkfood knowingly violated CPSA Section 15(b) and that it will recommend to the Commission a $900,000 civil penalty. We contend that the Commission's allegations are without merit.
Junkfood has subsequently responded to the Commission staff regarding its recommended penalty, setting forth a number of defenses and mitigating factors that could result in a much lower penalty, if any, ultimately imposed by a court should the matter proceed to litigation. Since then the Commission has requested additional information from Junkfood regarding the matter. While we will continue to defend against these allegations, we believe it is probable that a liability has been incurred. Based upon the terms of previously published CPSC settlements and related product recall notices, we believe if we settle the matter the minimum settlement amount would be $25,000. Should the Commission seek enforcement of the recommended civil penalty and ultimately prevail on its claims at trial, we could be required to pay amounts exceeding $900,000, along with interest and the Commission's costs and fees. During the quarter ended June 30, 2012, we recorded a liability for the most likely outcome within this range and this liability remains recorded as of June 29, 2013.
In addition, at times we are party to various legal claims, actions and complaints. We believe that, as a result of legal defenses, insurance arrangements, and indemnification provisions with parties believed to be financially capable, such actions should not have a material effect on our operations, financial condition, or liquidity.
ITEM 4. SUBMISSION OF MATTERS TO A VOTE OF SECURITY HOLDERS
No matters were submitted to a vote of security holders during the fourth quarter of our 2013 fiscal year.
PART II
| |
ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES. |
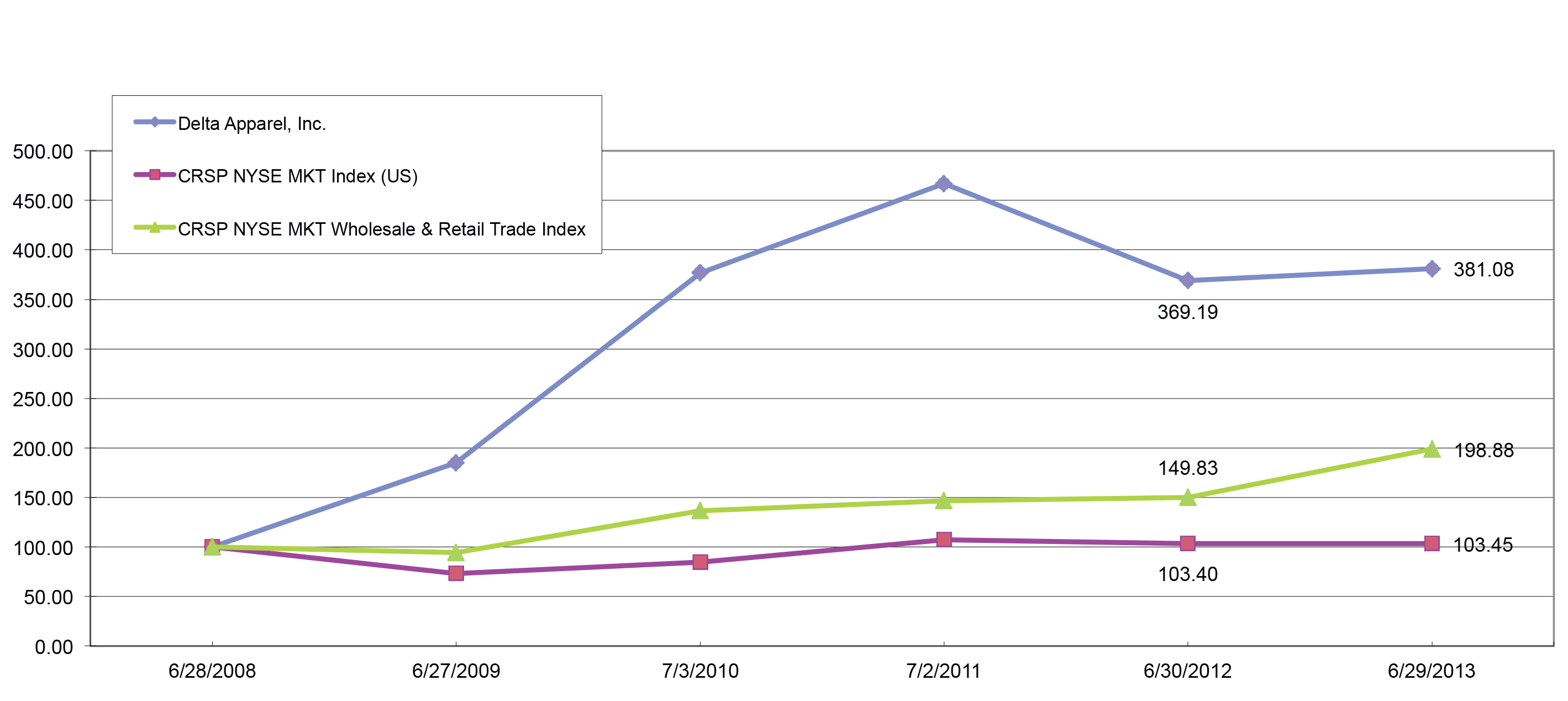
Market Information for Common Stock: The common stock of Delta Apparel, Inc. is listed and traded on the NYSE MKT under the symbol “DLA”. As of August 22, 2013, there were approximately 947 record holders of our common stock.
The following table sets forth, for each of the periods indicated below, the high and low sales prices per share of our common stock as reported on the NYSE MKT.
|
| | | | | | | |
| Fiscal Year 2013 | | Fiscal Year 2012 |
| High | | Low | | High | | Low |
First Quarter | $14.96 | | $12.65 | | $19.87 | | $14.24 |
Second Quarter | 15.78 | | 13.75 | | 19.74 | | 14.66 |
Third Quarter | 17.84 | | 13.50 | | 19.71 | | 14.01 |
Fourth Quarter | 16.95 | | 12.80 | | 17.22 | | 13.22 |
Dividends: Our Board of Directors did not declare, nor were any dividends paid, during fiscal years 2013 and 2012. Subject to the provisions of any outstanding blank check preferred stock (none of which is currently outstanding), the holders of our common stock are entitled to receive whatever dividends, if any, that may be declared from time to time by our Board of Directors in its discretion from funds legally available for that purpose. We are allowed to make cash dividends and stock repurchases if (i) as of the date of the payment or repurchase and after giving effect to the payment or repurchase, we have availability on that date of not less than $15 million and average availability for the 30 day period immediately preceding that date of not less than $15 million; and (ii) the aggregate amount of dividends and stock repurchases after May 27, 2011 does not exceed $19 million plus 50% of our cumulative net income (as defined in the Amended Loan Agreement) from the first day of fiscal year 2012 to the date of determination. At June 29, 2013 and July 30, 2012, there was $11.6 million and $14.8 million, respectively, of retained earnings free of restrictions to make cash dividends or stock repurchases.
We would expect that our Board of Directors would consider the advisability of instituting a dividend program in the future. Any future cash dividend payments will depend upon our earnings, financial condition, capital requirements, compliance with loan covenants and other relevant factors.
Purchases of our Own Shares of Common Stock: See Note 14 - Repurchase of Common Stock and Note 8 - Debt, in Item 15, which is incorporated herein by reference.
Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans: The information required by Item 201(d) of Regulation S-K is set forth under “Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters” of this Annual Report, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
Comparison of Total Return Among Delta Apparel, Inc., CRSP NYSE MKT Index (US), and CRSP NYSE MKT Wholesale & Retail Trade Index: Our common stock began trading on the NYSE MKT (previously the NYSE Amex) on June 30, 2000, the last trading day of our fiscal year 2000. Prior to that date, no securities of Delta Apparel were publicly traded. Set forth below is a line graph comparing the yearly change in the cumulative total stockholder return, assuming dividend reinvestment, of our common stock with (1) the CRSP NYSE MKT Index (US) and (2) the CRSP NYSE MKT Wholesale and Retail Trade Index, which is comprised of all NYSE MKT companies with SIC codes from 5000 through 5999. This performance graph assumes that $100 was invested in the common stock of Delta Apparel and comparison groups on June 28, 2008, and that all dividends have been reinvested.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2008 | | 2009 | | 2010 | | 2011 | | 2012 | | 2013 |
Delta Apparel, Inc. | $ | 100.00 |
| | $ | 185.14 |
| | $ | 376.76 |
| | $ | 466.76 |
| | $ | 369.19 |
| | $ | 381.08 |
|
CRSP NYSE MKT Index (US) | $ | 100.00 |
| | $ | 73.07 |
| | $ | 84.85 |
| | $ | 107.15 |
| | $ | 103.40 |
| | $ | 103.45 |
|
CRSP NYSE MKT Wholesale & Retail Trade Index | $ | 100.00 |
| | $ | 94.37 |
| | $ | 136.34 |
| | $ | 146.82 |
| | $ | 149.83 |
| | $ | 198.88 |
|
| |
ITEM 6. | SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA |
See information regarding our acquisitions within “Item 1. Business” under the heading “Acquisitions”. The selected financial data includes the financial position and results of operations of acquired businesses beginning on the date of acquisition. The consolidated statements of operations data for the years ended June 27, 2009 and July 3, 2010, and the consolidated balance sheet data as of June 27, 2009, July 3, 2010, and July 2, 2011, are derived from, and are qualified by reference to, our audited consolidated financial statements not included in this document. The consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended July 2, 2011, June 30, 2012, and June 29, 2013, and the consolidated balance sheet data as of June 30, 2012, and June 29, 2013, are derived from, and are qualified by reference to, our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this document. We operate on a 52-53 week fiscal year ending on the Saturday closest to June 30. All fiscal years shown were 52-week years with the exception of fiscal year 2010 which was a 53-week year. Historical results are not necessarily indicative of results to be expected in the future. The selected financial data should be read in conjunction with the Consolidated Financial Statements and the related notes as indexed on page F-1 and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in Item 7.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fiscal Year Ended |
| June 29, 2013 |
| | June 30, 2012 |
| | July 2, 2011 |
| | July 3, 2010 |
| | June 27, 2009 |
|
| (In thousands, except per share amounts) |
Statement of Operations Data: | | | | | | | | | |
Net sales | $ | 490,523 |
| | $ | 489,923 |
| | $ | 475,236 |
| | $ | 424,411 |
| | $ | 355,197 |
|
Cost of goods sold | (381,014 | ) | | (406,200 | ) | | (359,001 | ) | | (323,628 | ) | | (278,758 | ) |
Selling, general and administrative expenses | (94,944 | ) | | (89,973 | ) | | (91,512 | ) | | (80,695 | ) | | (64,388 | ) |
Valuation adjustment, net | — |
| | — |
| | 918 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Other income (expense), net | (662 | ) | | 28 |
| | (345 | ) | | 74 |
| | 96 |
|
Operating income (loss) | 13,903 |
| | (6,222 | ) | | 25,296 |
| | 20,162 |
| | 12,147 |
|
Interest expense, net | 3,997 |
| | 4,132 |
| | 2,616 |
| | 3,509 |
| | 4,718 |
|
Earnings (loss) before income taxes | 9,906 |
| | (10,354 | ) | | 22,680 |
| | 16,653 |
| | 7,429 |
|
Provision for (benefit from) income taxes | 722 |
| | (7,907 | ) | | 5,353 |
| | 4,466 |
| | 973 |
|
Net earnings (loss) | $ | 9,184 |
| | $ | (2,447 | ) | | $ | 17,327 |
| | $ | 12,187 |
| | $ | 6,456 |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
Basic earnings (loss) per common share: | $ | 1.12 |
| | $ | (0.29 | ) | | $ | 2.04 |
| | $ | 1.43 |
| | $ | 0.76 |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
Diluted earnings (loss) per common share: | $ | 1.08 |
| | $ | (0.29 | ) | | $ | 1.98 |
| | $ | 1.40 |
| | $ | 0.76 |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
Dividends declared per common share | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
|
| | | | | | | | | |
Balance Sheet Data (at year end): | | | | | | | | | |
Working capital | $ | 173,435 |
| | $ | 187,029 |
| | $ | 160,646 |
| | $ | 125,163 |
| | $ | 135,369 |
|
Total assets | 311,910 |
| | 320,394 |
| | 311,865 |
| | 251,333 |
| | 256,993 |
|
Total long-term debt, less current maturities | 94,763 |
| | 110,949 |
| | 83,974 |
| | 62,355 |
| | 85,936 |
|
Shareholders’ equity | 141,066 |
| | 138,967 |
| | 141,965 |
| | 125,714 |
| | 112,145 |
|
| |
ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
BUSINESS OUTLOOK
We had a good year across our business units, with the exception of Soffe. We have been busy working on a number of initiatives that should have a very positive effect on our results as we go forward.
Soffe's difficulties primarily stem from a high degree of turmoil that occurred in the mid-tier retail industry and our failure to make adjustments in our go-to-market strategy and operations in a timely manner to address changes in fashion and the market direction. Our management team continues to focus its attention to address the problems experienced at Soffe and to take steps to regain the sales and profitability we have historically enjoyed with the business.
During the year, we realigned our merchandising, marketing and sales leadership, who are focused on expanding the retail customer base and replacing the business we lost. We are excited about the new Soffe product line designed for spring 2014. We have shown the line to focus groups and key retailer accounts and have received very positive responses.
We have modernized Soffe's screen print operations and on July 10, 2013 announced the closing of the Wendell, North Carolina decoration facility to consolidate these operations into the Fayetteville facility. This will improve Soffe's printing capabilities and should save approximately $1.5 million annually beginning in September 2013. We are in the process of implementing improved systems and business processes to streamline our operations so they run more efficiently. Although it will take some time before we see the full benefits of these changes in our results, we should begin seeing improved operating margins as the 2014 fiscal year progresses. We also took steps to reduce our selling, general and administrative headcounts at Soffe and continue to work on additional measures to lower these costs.
Our other business units performed well during the year, growing sales and expanding margins from improved manufacturing performance and successful merchandising initiatives. We began the consolidation of our bookstore business into The Game. We recently introduced a new collegiate apparel line under The Game, “American Threads”, a 100% made in the USA collection. The line just hit stores, but appears to be well-received by college students. We are also getting interest from other customers regarding the 'Made in the USA' apparel and headwear products, creating another potential growth avenue for Delta Apparel.
The Junkfood business continued its growth in 2013 as well. We continue to build the Junk Food brand with direct-to-consumer business, and will continue this in fiscal year 2014 with the opening of a Junk Food flagship retail store on Abbot Kinney Boulevard in Venice, California. The store will embrace the full lifestyle approach and, in addition our Junkfood graphic products and our new Stray Heart product line of contemporary non-graphic women's apparel, will offer contemporary brands in other product categories so the customer can purchase all the essentials for a complete outfit at our Junk Food store. In conjunction with the new retail store, Junkfood is also re-launching its ecommerce site to take advantage of new technology. The new site will feature a wider array of products, both Junkfood and Stray Heart, along with web-exclusive opportunities. In addition, the site will have enhanced functionality with ease of navigation for an ultimate Junkfood experience.
During fiscal year 2013 in our basics segment, we completed the conversion of FunTees to the Catalog ERP platform, allowing us to streamline operations, consolidate administrative functions, and reduce general and administrative costs. With this we are able to provide broader offerings to our customers using off-the-shelf blanks combined with our decoration and retail packaging services. This has allowed us to gain market share with retail licensing customers, who previously had to dual source products. We anticipate the convenience and wider range of offerings will continue to gain traction with customers, driving continued growth in the basics segment.
During the year we also completed the move of our print development offshore and have doubled the size of our El Salvador screen printing operations. The resources that we have invested in printing provide us with new technologies and printing techniques that should enable us to satisfy the growing demand for decoration services. Our manufacturing expansion project is also currently underway. We are expanding textile operations at our Ceiba Textile plant in Honduras, as well as expanding sewing operations in that country. As output from these facilities is increased, it will leverage our fixed costs driving lower product costs and improved margins.
In January 2013, we opened a third-party operated distribution center in Canada to support the growing customer base in that country. We are taking a further step to broaden our footprint with a distribution center in Dallas, Texas. The Dallas distribution facility will be third-party operated, minimizing the need for capital investment on our part. Serving key markets throughout Texas and surrounding states, it will enable us to offer one day shipping to customers as well as serving as a customer pick-up point in that location. In addition to better serving our existing customer base and providing a platform to attract new customers, the new distribution center should also lower our overall freight cost to customers in the Southwest. We expect to begin shipping from the facility by December 2013 and be fully functional for the spring selling season.
On August 27, 2013 we completed the acquisition of the assets of Salt Life Holdings, LLC, including all domestic and international trademark rights to the Salt Life brand. We are excited to add this fast-growing lifestyle brand to our portfolio of brands. The purchase price consisted of $15 million of cash, two promissory notes in the aggregate amount of $22 million, and a contingent payment if certain performance targets are met with respect to sales levels in calendar 2019. We financed the cash portion of the purchase price through an amendment to our U.S. asset-based secured revolving credit facility.
Having worked with Salt Life under a license agreement for the past two years, we have grown the geographic distribution of the brand from a single market in Florida, to more than 1,500 retail doors from Texas up the coast to the Northeast. The acquisition of Salt Life continues our strategy of building lifestyle brands that take advantage of our creative capabilities, vertical manufacturing platform and international sourcing competencies. We are excited about the opportunities we have as owners of the Salt Life brand. We plan to greatly increase the investment in consumer advertising and point of sale branding to further build core consumer appeal for each of the groups of Salt Life enthusiasts - surfers, divers, fishermen and beach goers, and the millions of other consumers who long to live the Salt Life. While this acquisition will have minimal impact on our revenue and earnings in the upcoming year, we expect it to be a key growth catalyst in the future. We look forward to the many opportunities we will build upon for strong continued growth with the Salt Life brand.
We have also decided to change our fiscal year-end from June to September. This move will better align our planning, financial and reporting functions with the seasonality of the business and should provide investors with more timely information that better reflects the operations of the business. From now on, our fiscal year will end on the Saturday closest to September 30. We will have a three-month bridge period ending on September 28, 2013. Our fiscal 2014 will then begin on September 29, 2013 and end on September 27, 2014.
EARNINGS GUIDANCE
For the three month bridge period ending September 28, 2013, we expect sales in the range of $130 million to $132 million. We are expecting continued sales growth in each of our business units except Soffe, which is expected to have continued softness through the fall. Earnings are expected to be $0.30 to $0.35 per share in this three month period. This includes approximately $0.14 per share of one-time costs, comprising $0.11 related to the Wendell closing and $0.03 related to the Salt Life acquisition.
For the new fiscal year ending September 27, 2014, we anticipate revenue to be in the $500 to $510 million range and earnings to come in at $2.00 to $2.10 per diluted share.
Our fiscal year 2014 guidance is based on the following assumptions:
| |
• | Organic sales growth in each of our business units. The sales growth is expected to come from higher volumes, which in some cases will be offsetting lower average selling prices. |
| |
• | Cotton remains at the current prices in the mid-80 cent range with basic tee prices remain level. While cotton prices have moderated considerably from the volatility experienced in the past two years, speculators in the market and potential changes in China's cotton policy continue to make cotton prices quite volatile. |
| |
• | Selling, general and administration costs to decrease as a percentage of sales by up to 50 basis points even with increased marketing in our brands, especially Salt Life, in the upcoming year. |
| |
• | Gross margins continue to improve in the 100 to 200 basis points range driven by improved manufacturing costs as we gain efficiencies and further leverage the fixed expenses with our planned manufacturing expansion. The improved gross margins would be recognized in the second half of the fiscal year. |
| |
• | Increased interest expense based on the higher debt levels from the Salt Life acquisition, including the non-cash interest expense recorded on the zero-interest promissory notes. |
| |
• | An effective tax rate between 22 and 24%. |
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Overview
Fiscal year 2013 marked another year of growth for Delta Apparel, Inc. and our tenth consecutive year of record revenue. Strong net sales growth in our basics segment along with Junkfood, The Game and Art Gun drove the record revenue. These gains were offset by softness in the Soffe business that continued through the fiscal year.
Gross margins in the basics segment improved 1,200 basis points in fiscal year 2013 as we benefited from manufacturing efficiencies and cost-savings initiatives. In addition, the prior year had been impacted by the effects resulting from the high cotton costs. Gross margins also expanded in each of the branded business units, besides Soffe, from effective merchandising strategies.
Operating profit increased to $13.9 million, or 2.8% of sales, resulting in net earnings of $9.2 million, or $1.08, per diluted share compared to an operating loss of $6.2 million, or $0.29 per diluted share, in fiscal year 2012.
Quarterly Financial Data
For information regarding quarterly financial data, refer to Note 16 - Quarterly Financial Information (Unaudited) to the Consolidated Financial Statements, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
Fiscal Year 2013 versus Fiscal Year 2012
Net sales for fiscal year 2013 were $490.5 million, a $0.6 million, or 0.1%, increase from the prior year sales of $489.9 million, all of which was organic sales growth. The basics segment's 14% increase in unit sales was partially offset by lower average selling prices, resulting in 6.3% sales growth, bringing sales to $270.9 million. Sales in the branded segment declined 6.6% to $219.6 million. Junk Food® apparel and the Salt Life® collection, along with Art Gun, had strong sales growth, which was offset by lower sales of Soffe® merchandise.
Gross margins increased 520 basis points to 22.3% of net sales in fiscal year 2013 from 17.1% of net sales in the prior year. The prior year gross margins were negatively impacted by the effect that high cotton prices were having on our industry. Our gross margins may not be comparable to other companies, since some companies include costs related to their distribution network in cost of goods sold and we exclude them from gross profit and include them in selling, general and administrative expenses.
Fiscal year 2013 selling, general and administrative expenses were $94.9 million, or 19.4% of sales, compared to $90.0 million, or 18.4% of sales, in the prior year. The increase in selling, general and administrative expenses is primarily from an increase in performance-based compensation expense resulting from the improvement in earnings during fiscal year 2013 compared to the prior year. In addition, fiscal year 2013 included $1.2 million of cost associated with previously disclosed internal investigation by the Audit Committee related to fiscal year 2012.
Fiscal year 2013 operating income was $13.9 million, or 2.8% of sales, compared to a $6.2 million operating loss, or 1.3% of sales, in fiscal year 2012 resulting from the factors described above. Operating income of $15.8 million in the basics segment was partially offset by a $1.9 million loss in the branded segment, resulting from softness in the Soffe business.
Net interest expense for fiscal year 2013 was $4.0 million, a decrease of $0.1 million, from $4.1 million for fiscal year 2012.
Our fiscal year 2013 effective income tax rate was 7.3% compared to an effective tax rate of 76.4% which resulted in a tax benefit in fiscal year 2012. We benefit from having income in foreign jurisdictions that are either exempt from income taxes or have tax rates lower than the United States. The tax benefit in fiscal year 2012 was impacted by the operating losses driven by the inventory markdown during the year which lowered our U.S. taxable income while maintaining profits in the offshore taxable and tax-free jurisdictions.
Fiscal year 2013 had a net earnings of $9.2 million, a $11.6 million increase from the net loss of $2.4 million in fiscal year 2012.
Fiscal Year 2012 versus Fiscal Year 2011
Net sales for fiscal year 2012 were $489.9 million, a $14.7 million, or 3.1%, increase from the prior year sales of $475.2 million, all of which was organic sales growth. Both the basics and branded segments contributed to the increase, with an 0.5% increase in our basics segment and a 6.1% increase in our branded segment. Sales in the branded segment were $235.2 million, or approximately 48% of total sales. Junk Food® apparel and the growth of the Salt Life® collection contributed to the increased sales, which was partially offset by lower sales of Soffe® merchandise. Sales within the basics segment increased to $254.7 million, or 52% of our total revenue. The 0.5% organic growth in the basics segment was driven by a 6.2% increase in average selling prices, partially offset by a decline in units sold.
Gross margins declined 740 basis points to 17.1% of net sales in fiscal year 2012 from 24.5% of net sales in the prior year. The decrease in gross profit as a percentage of sales was driven primarily from the impact of higher raw material prices in both the branded and basics segment. The decrease in margins for the year was accelerated in the second fiscal quarter when we took a $16.2 million inventory markdown in the basics segment, an action taken to account for the negative effect that cotton prices were having on our industry. Our gross margins may not be comparable to other companies, since some companies include costs related to their distribution network in cost of goods sold and we exclude them from gross profit and include them in selling, general and administrative expenses.
Fiscal year 2012 selling, general and administrative expenses were $90.0 million, or 18.4% of sales, compared to $91.5 million, or 19.3% of sales, in the prior year. The decline in selling, general and administrative expenses is primarily from a decrease in performance-based compensation expense resulting from the decline in earnings during fiscal year 2012 compared to the prior year. In addition, fiscal year 2011 included costs associated with the acquisition of The Cotton Exchange, as well as some brand-marketing campaigns that were not repeated in fiscal year 2012.
Fiscal year 2012 resulted in an operating loss of $6.2 million, or 1.3% of sales, in fiscal year 2012, compared to an operating profit of $25.3 million, or 5.3% of sales, in fiscal year 2011 resulting from the factors described above. Operating income in the branded segment was $6.3 million, while the basics segment generated a loss of $12.5 million.
Net interest expense for fiscal year 2012 was $4.1 million, an increase of $1.5 million, or 57.9%, from $2.6 million for fiscal year 2011. The increase in net interest expense was primarily due to higher debt levels resulting from the additional working capital requirements from the higher raw material costs. In addition, average interest rates rose approximately 70 basis points, further increasing interest expense in fiscal year 2012.
Our fiscal year 2012 effective income tax rate was 76.4% compared to an effective tax rate of 23.6% in fiscal year 2011. The tax rate was impacted by the operating losses driven by the inventory markdown during the year, lowering our U.S. taxable income while maintaining profits in the offshore taxable and tax-free jurisdictions
Fiscal year 2012 had a net loss of $2.4 million, a $19.8 million decrease from net earnings of $17.3 million in fiscal year 2011.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Credit Facility and Other Financial Obligations
On May 27, 2011, Delta Apparel, Soffe (successor by merger to TCX, LLC), Junkfood, To The Game and Art Gun entered into a Fourth Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement (the “Amended Loan Agreement”) with the financial institutions named in the Amended Loan Agreement as Lenders, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Administrative Agent, Bank of America, N.A., as Syndication Agent, Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Sole Lead Arranger, and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC and Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as Joint Bookrunners.
Pursuant to the Amended Loan Agreement, the line of credit is $145 million (subject to borrowing base limitations), and matures on May 26, 2016. Provided that no event of default exists, we have the option to increase the maximum credit available under the facility to $200 million (subject to borrowing base limitations), conditioned upon the Agent's ability to secure additional commitments and customary closing conditions. At June 29, 2013, we had $88.8 million outstanding under our U.S. revolving credit facility at an average interest rate of 2.6%, and had the ability to borrow an additional $42.0 million.
For further information regarding our U.S. asset-based secured credit facility, refer to Note 8 - Long-Term Debt and Note 17 - Subsequent Events to the Consolidated Financial Statements, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
In the third quarter of fiscal year 2011, we renegotiated our loan agreement with Banco Ficohsa, a Honduran bank. Proceeds from the new loan agreement were used to extinguish the existing loan indebtedness and resulted in no gain or loss being recorded upon extinguishment. As of June 29, 2013, we had a total of $9.5 million outstanding on this loan. For further information regarding our Honduran credit facility, refer to Note 8 - Long-Term Debt to the Consolidated Financial Statements, which information is incorporated herein by reference.
Our primary cash needs are for working capital and capital expenditures, as well as to fund share repurchases under our Stock Repurchase Program. In addition, in the future we may use cash to pay dividends.
Derivative Instruments
From time to time we may use derivative instruments to manage our exposure to interest rates. These financial instruments are not used for trading or speculation purposes. When we enter into a derivative instrument, we determine whether hedge accounting can be applied. Where hedge accounting can be applied, a hedge relationship is designated as either a fair value hedge or cash flow hedge. The hedge is documented at inception, detailing the particular risk objective and strategy considered for undertaking the hedge. The documentation identifies the specific asset or liability being hedged, the risk being hedged, the type of derivative used and how effectiveness of the hedge will be assessed.
On September 1, 2011, we entered into three interest rate swap agreements, as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| Effective Date | | Notational Amount | | LIBOR Rate | | Maturity Date |
Interest Rate Swap | 9/1/2011 | | $10 million | | 0.7650 | % | | 9/1/2013 |
Interest Rate Swap | 9/1/2011 | | $10 million | | 0.9025 | % | | 3/1/2014 |
Interest Rate Swap | 9/1/2011 | | $10 million | | 1.0700 | % | | 9/1/2014 |
We assessed these agreements and concluded that the swap agreements match the exact terms of the underlying debt except for a slight timing difference. We use a hypothetical derivative method to assess and measure ineffectiveness associated with the hedge each reporting period. During fiscal years 2013 and 2012, the interest rate swap agreements had minimal ineffectiveness and were considered highly-effective hedges.
Changes in the derivatives’ fair values are deferred and are recorded as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (“AOCI”), net of income taxes, until the underlying transaction is recorded. When the hedged item affects income, gains or losses are reclassified from AOCI to the Consolidated Statements of Operations as interest income/expense. Any ineffectiveness in our hedging relationships is recognized immediately in the Consolidated Statement of Operations. The changes in fair value of the interest rate swap agreements resulted in an AOCI gain, net of taxes, of $47 thousand for the year ended June 29, 2013 and an AOCI loss, net of taxes, of $0.1 million the year ended June 30, 2012.
Operating Cash Flows
In fiscal year 2013, operating activities provided $32.2 million in cash compared to $19.1 million in cash used by operating activities for fiscal year 2012. The improvement in operating cash flow during fiscal year 2013 from the prior year resulted from stronger operating earnings, lower inventory costs, the tax refund received from the carryback of the 2012 net operating loss, and higher accounts payable and accrued liabilities. The cash flow used by operating activities in fiscal year 2012 resulted from our net loss combined with lower accounts payable, taxes payable and accrued expenses.
Investing Cash Flows
Cash used in investing activities in fiscal year 2013 was $7.9 million compared to $6.6 million in fiscal year 2012. In fiscal year 2013, we used $7.9 million in cash for the purchase of property and equipment primarily to improve our information technology in both our branded and basics segments, to increase our post-production decorating and warehouse capacity, and to lower costs in our manufacturing facilities, which support both our branded and basics segments. In fiscal year 2012, we used $6.6 million for the purchase of property and equipment primarily to improve our manufacturing platform and business operating systems.
We expect to spend approximately $14 million in capital expenditures in fiscal year 2014, most of which will focus on expansion in both our international and U.S. manufacturing and decoration facilities and improvements to our business operating systems.
Financing Activities
Cash used by financing activities was $24.2 million in fiscal year 2013 compared to cash provided by financing activities of $25.5 million in fiscal year 2012. In fiscal year 2013, we used cash to reduce our outstanding debt and for the purchase of our common stock. In fiscal year 2012, the cash was primarily provided from our U.S. revolving credit facility and used for working capital, for capital expenditures and for the purchase of our common stock.
Future Liquidity and Capital Resources
Based on our expectations, we believe that our credit facility should be sufficient to satisfy our foreseeable working capital needs, and that the cash flow generated by our operations and funds available under our credit line should be sufficient to service our debt payment requirements, to satisfy our day-to-day working capital needs and to fund our planned capital expenditures. Any material deterioration in our results of operations, however, may result in our losing the ability to borrow under our revolving credit facility and to issue letters of credit to suppliers, or may cause the borrowing availability under our facility to be insufficient for our needs.
The following table summarizes our contractual cash obligations, as of June 29, 2013, by future period.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payments Due by Period (in thousands) |
| Total | | Less than 1 year | | 1 - 3 years | | 3 – 5 years | | After 5 years |
Contractual Obligations: | | | | | | | | | |
Long-term debt (a) | $ | 98,292 |
| | $ | 3,529 |
| | $ | 88,143 |
| | $ | 6,620 |
| | $ | — |
|
Operating leases | 23,951 |
| | 8,353 |
| | 12,650 |
| | 2,948 |
| | — |
|
Capital leases | 9 |
| | 9 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Letters of credit | 1,037 |
| | 1,037 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Minimum royalty payments | 6,186 |
| | 3,100 |
| | 3,086 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Purchase obligations | 43,616 |
| | 43,616 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Total (b) | $ | 173,091 |
| | $ | 59,644 |
| | $ | 103,879 |
| | $ | 9,568 |
| | $ | — |
|
______________________
| |
(a) | We exclude interest payments from these amounts because the cash outlay for the interest is unknown and cannot be reliably estimated because the majority of the debt is under a revolving credit facility. Interest payments will be determined based upon the daily outstanding balance of the revolving credit facility and the prevailing interest rate during that time. |
| |
(b) | We excluded deferred income tax liabilities of $4.5 million from the contractual cash obligations table because we believe inclusion would not be meaningful. Refer to Note 9 - Income Taxes to our Consolidated Financial Statements for more information on our deferred income tax liabilities. Deferred income tax liabilities are calculated based on temporary differences between tax bases of assets and liabilities and their respective book bases, which will result in taxable amounts in future years when the liabilities are settled at their reported financial statement amounts. The results of these calculations do not have a direct connection with the amount of cash taxes to be paid in any future periods and therefore would not relate to liquidity needs. As a result, including deferred income tax liabilities as payments due by period in the schedule could be misleading. |
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of June 29, 2013, we do not have any off-balance sheet arrangements that are material to our financial condition, results of operations or cash flows as defined by Item 303(a)(4) of Regulation S-K promulgated by the SEC other than the letters of credit, operating leases, and purchase obligations described above. We have entered into derivative interest rate contracts as described and included below in “Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk” in Item 7A of this report.
Dividends and Purchases of our Own Shares
We are allowed to make cash dividends and stock repurchases if (i) as of the date of the payment or repurchase and after giving effect to the payment or repurchase, we have availability on that date of not less than $15 million and average availability for the 30 day period immediately preceding that date of not less than $15 million; and (ii) the aggregate amount of dividends and stock repurchases after May 27, 2011 does not exceed $19 million plus 50% of our cumulative net income (as defined in the Amended Loan Agreement) from the first day of fiscal year 2012 to the date of determination. At June 29, 2013 and July 30, 2012, there was $11.6 million and $14.8 million, respectively, of retained earnings free of restrictions to make cash dividends or stock repurchases.
Our Board of Directors did not declare, nor were any dividends paid, during fiscal years 2013 and 2012. We would expect that our Board of Directors would consider the advisability of instituting a dividend program in the future. Any future cash dividend payments will depend upon our earnings, financial condition, capital requirements, compliance with loan covenants and other relevant factors.
As of June 30, 2012, our Board of Directors had authorized management to use up to $20.0 million to repurchase stock in open market transactions under our Stock Repurchase Program. On January 23, 2013, the Board of Directors authorized an additional $10.0 million for share repurchases, bringing the aggregate total authorized to $30.0 million. During fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011, we purchased 544,576 shares, 168,120 shares and 176,756 shares, respectively, of our common stock for a total cost of $7.8 million, $2.6 million and $2.5 million, respectively. As of June 29, 2013, we have purchased 1,914,223 shares of common stock for an aggregate of $22.0 million since the inception of the Stock Repurchase Program. All purchases were made at the discretion of management and pursuant to the safe harbor provisions of SEC Rule 10b-18. As of June 29, 2013, $8.0 million remained available for future purchases under our Stock Repurchase Program, which does not have an expiration date.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are based upon our Consolidated Financial Statements, which were prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). The preparation of our Consolidated Financial Statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. We base our estimates and judgments on historical experience and various other factors that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions. Our most critical accounting estimates, discussed below, pertain to revenue recognition, accounts receivable and related reserves, inventory and related reserves, the carrying value of goodwill, and the accounting for income taxes.
Note 2 to our Consolidated Financial Statements includes a summary of the significant accounting policies or methods used in the preparation of our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Revenue Recognition
Revenues from product sales are recognized when ownership is transfered to the customer, which includes not only the passage of title, but also the transfer of the risk of loss related to the product. At this point, the sales price is fixed and determinable, and we are reasonably assured of the collectibility of the sale. The majority of our sales are shipped FOB shipping point and revenue is therefore recognized when the goods are shipped to the customer. For sales that are shipped FOB destination point, we do not recognize the revenue until the goods are received by the customer. Shipping and handling charges billed to our customers are included in net revenue and the related costs are included in cost of goods sold. Revenues are reported on net sales basis, which is computed by deducting product returns, discounts and estimated returns and allowances. We estimate returns and allowances on an ongoing basis by considering historical and current trends.
Royalty revenue is primarily derived from royalties paid to us by licensees of our intellectual property rights, which include, among other things, trademarks and copyrights. We execute license agreements with our licensees detailing the terms of the licensing arrangement. Royalties are generally recognized upon receipt of the licensees' royalty report, in accordance with the terms of the executed license agreement, and when all other revenue recognition criteria have been met.
Accounts Receivable and Related Reserves
In the normal course of business, we extend credit to our customers based upon defined credit criteria. Accounts receivable, as shown on our Consolidated Balance Sheets, are net of related reserves. We estimate the net collectibility of our accounts receivable and establish an allowance for doubtful accounts based upon this assessment. In situations where we are aware of a specific customer’s inability to meet its financial obligation, such as in the case of a bankruptcy filing, a specific reserve for bad debts is recorded against amounts due to reduce the net recognized receivable to the amount reasonably expected to be collected. For all other customers, reserves are determined through analysis of the aging of accounts receivable balances, historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit-worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customer payment terms. In addition, reserves are established for other concessions that have been extended to customers, including advertising, markdowns and other accommodations, net of historical recoveries. These reserves are determined based upon historical deduction trends and evaluation of current market conditions. Significant changes in customer concentration or payment terms, deterioration of customer credit-worthiness or further weakening in economic trends could have a significant impact on the collectibility of receivables and our operating results.
Inventories and Related Reserves
We state inventories at the lower of cost or market using the first-in, first-out method. Inventory cost includes materials, labor and manufacturing overhead on manufactured inventory, and all direct and associated costs, including inbound freight, to acquire sourced products. We regularly review inventory quantities on hand and record reserves for obsolescence, excess quantities, irregulars and slow moving inventory based on historical selling prices, current market conditions, and forecasted product demand to reduce inventory to its net realizable value. If actual selling prices are less favorable than those projected, or if sell-through of the inventory is more difficult than anticipated, additional inventory reserves may be required.
During the second quarter of fiscal year 2012, we recorded a $16.2 million lower of cost or market write-down on the inventory in the basics segment and its firm purchase commitments for yarn resulting from historically high cotton prices in its inventory costs combined with declining selling prices. The estimation of the total write-down involved management judgments and assumptions including assumptions regarding future selling price forecasts, the allocation of raw materials between business units, the estimated costs to complete, disposal costs and a normal profit margin. The inventory and yarn firm purchase commitments associated with this inventory write-down was sold during our fiscal year 2012.
Goodwill and Contingent Consideration
Goodwill and definite-lived intangibles were recorded in conjunction with our acquisitions of Junkfood Clothing Company and Art Gun. We did not record any separately identifiable indefinite-lived intangibles associated with either of these acquisitions. Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price and related costs over the value assigned to net tangible and identifiable intangible assets of businesses acquired. Goodwill must be tested for impairment at least annually, or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount may be impaired, and is required to be written down when impaired. The goodwill impairment testing process involves the use of significant assumptions, estimates and judgments with respect to a variety of factors, including sales, gross margins, selling, general and administrative expenses, capital expenditures, cash flows and the selection of an appropriate discount rate, all of which are subject to inherent uncertainties and subjectivity. When we perform goodwill impairment testing, our assumptions are based on annual business plans and other forecasted results, which we believe represent those of a market participant. We select a discount rate, which is used to reflect market-based estimates of the risks associated with the projected cash flows, based on the best information available as of the date of the impairment assessment. In our second quarter of fiscal year 2011, we identified indicators of impairment on the Art Gun goodwill. The test of impairment indicated that the goodwill at Art Gun was fully impaired, resulting in a $0.6 million impairment charge recorded in the fiscal quarter ended January 1, 2011.
See Note 2(m) - Significant Accounting Policies to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further information regarding our remeasurement of contingent consideration and testing for goodwill impairment, which information is herein incorporated by reference.
Given the current macro-economic environment and the uncertainties regarding its potential impact on our business, there can be no assurance that our estimates and assumptions used in our impairment tests will prove to be accurate predictions of the future. If our assumptions regarding forecasted cash flows are not achieved, it is possible that an impairment review may be triggered and goodwill may be determined to be impaired.
Income Taxes
We account for income taxes under the liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases, and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. In fiscal year 2012, we generated federal net operating losses of $20.0 million. This net operating loss was classified in income tax receivable at June 30, 2012. When we filed our fiscal year end 2012 tax return, we carried back the net operating loss against the taxable income from fiscal years 2011 and 2010. The remaining $0.9 million of operating loss is classified in the income tax receivable at June 29, 2013 as it will be applied against our fiscal year 2013 taxable income.
We established a valuation allowance related to certain of our state operating loss carryforward amounts in accordance with the provisions of the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") Codification No. 740, Income Taxes (“ASC 740”). We continually review the adequacy of the valuation allowance and recognize the benefits of deferred tax assets if reassessment indicates that it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will be realized based on earnings forecasts in the respective state tax jurisdictions. We had state net operating loss carryforwards (“NOLs”) in fiscal years 2013 and 2012 of approximately $31.6 million and $31.1 million, respectively. We had deferred tax assets of $1.4 million for both fiscal years 2013 and 2012 related to these state NOLs, with related valuation allowances against them of approximately $0.2 million and $0.1 million as of June 29, 2013 and June 30, 2012, respectively. These net loss carryforwards expire at various intervals through 2032.
RECENT ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
For information regarding recently issued accounting standards, refer to Note 2(z) and Note 2(aa) to our Consolidated Financial Statements.
| |
ITEM 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
Commodity Risk Sensitivity
We have a supply agreement with Parkdale to supply our yarn requirements until December 31, 2015. Under the supply agreement, we purchase from Parkdale all of our yarn requirements for use in our manufacturing operations, excluding yarns that Parkdale does not manufacture or cannot manufacture due to temporary capacity constraints. The purchase price of yarn is based upon the cost of cotton plus a fixed conversion cost. Thus, we are subject to the commodity risk of cotton prices and cotton price movements, which could result in unfavorable yarn pricing for us. We fix the cotton prices as a component of the purchase price of yarn, pursuant to the supply agreement, in advance of the shipment of finished yarn from Parkdale. Prices are set according to prevailing prices, as reported by the New York Cotton Exchange, at the time we elect to fix specific cotton prices.
Yarn with respect to which we have fixed cotton prices at June 29, 2013 was valued at $14.4 million, and is scheduled for delivery between July 2013 and September 2013. At June 29, 2013, a 10% decline in the market price of the cotton covered by our fixed price yarn would have had a negative impact of approximately $1.1 million on the value of the yarn. This compares to what would have been a negative impact of $1.6 million at the 2012 fiscal year end based on the yarn with fixed cotton prices at June 30, 2012. The impact of a 10% decline
in the market price of the cotton covered by our fixed price yarn would have been less at June 29, 2013 than at June 30, 2012 due to lower cotton commitments at June 29, 2013 compared to June 30, 2012.
We may use derivatives, including cotton option contracts, to manage our exposure to movements in commodity prices. We do not designate our options as hedge instruments upon inception. Accordingly, we mark to market changes in the fair market value of the options in cost of sales in the Consolidated Statements of Operation. We did not own any significant cotton options contracts on June 29, 2013 or June 30, 2012.
If Parkdale’s operations are disrupted and it is not able to provide us with our yarn requirements, we may need to obtain yarn from alternative sources. Although alternative sources are presently available, we may not be able to enter into short-term arrangements with substitute suppliers on terms as favorable as our current terms with Parkdale. In addition, the cotton futures we have fixed with Parkdale may not be transferable to alternative yarn suppliers. Because there can be no assurance that we would be able to pass along the higher cost of yarn to our customers, this could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Interest Rate Sensitivity
Our U.S. revolving credit facility provides that the outstanding amounts owed shall bear interest at variable rates. If the amount of outstanding floating rate indebtedness at June 29, 2013 under the U.S. revolving credit facility had been outstanding during the entire year and the interest rate on this outstanding indebtedness was increased by 100 basis points, our expense would have increased by approximately $0.6 million, or 14.7%, for the fiscal year. This compares to an increase of $0.7 million, or 17.9%, for the 2012 fiscal year based on the outstanding floating rate indebtedness at June 30, 2012. The effect of a 100 basis point increase in interest rates would have had a lower dollar impact for the year ended June 29, 2013 compared to the year ended June 30, 2012 due to the lower debt levels outstanding on June 29, 2013. The percentage increase is less significant for fiscal year 2013 than for fiscal year 2012 because our total interest expense for fiscal year 2013 was lower than our total interest expense for fiscal year 2012. The actual increase in interest expense resulting from a change in interest rates would depend on the magnitude of the increase in rates and the average principal balance outstanding.
Derivatives
From time to time, we may use interest rate swaps or other instruments to manage our interest rate exposure and reduce the impact of future interest rate changes. See Note 2(y) and Note 15(d) to the Consolidated Financial Statements for more information on our derivatives.
| |
ITEM 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
Our Consolidated Financial Statements for each of the fiscal years in the three-year period ended June 29, 2013, together with the Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm thereon, are included in this report commencing on page F-1 and are listed under Part IV, Item 15 in this report.
| |
ITEM 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
Not applicable.
| |
ITEM 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as of June 29, 2013, and, based on their evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that these controls and procedures were effective at the evaluation date.
Disclosure controls and procedures are controls and other procedures that are designed to reasonably assure that information required to be disclosed in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the Securities and Exchange Commission’s rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information that we are required to disclose in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management of Delta Apparel, Inc. is responsible for establishing and maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. Our internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the preparation and fair presentation of published financial statements. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Financial Officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of June 29, 2013, based on the framework in Internal Control – Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The scope of our efforts to comply with the internal requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxely Act of 2002 with respect to fiscal year 2013 included all of our operations. Based on our evaluation, our management has concluded that, as of June 29, 2013, our internal control over financial reporting is effective.
The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of June 29, 2013, has been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm, who also audited our Consolidated Financial Statements. Ernst & Young’s attestation report on our internal controls over financial reporting is included herein.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There was no change in our internal control over financial reporting during the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2013 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders of Delta Apparel, Inc. and subsidiaries
We have audited Delta Apparel, Inc. and subsidiaries' internal control over financial reporting as of June 29, 2013, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (1992 framework) (the COSO criteria). Delta Apparel, Inc. and subsidiaries' management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management's Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the company's internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company's internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company's internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the company's assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, Delta Apparel, Inc. and subsidiaries maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of June 29, 2013, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of Delta Apparel, Inc. and subsidiaries as of June 29, 2013, and June 30, 2012, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, shareholders' equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended June 29, 2013, of Delta Apparel, Inc. and subsidiaries, and our report dated August 29, 2013, expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Atlanta, Georgia
August 29, 2013
| |
ITEM 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION |
Not applicable.
PART III
| |
ITEM 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference from the portions of the definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days following the end of our 2013 fiscal year under the headings “Corporate Governance”, “Executive Officers” and “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance.”
All of our employees, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer (who is also our principal accounting officer), are required to abide by our business conduct policies so that our business is conducted in a consistently legal and ethical manner. We have adopted a code of business conduct and ethics known as our Ethics Policy Statement. The Ethics Policy Statement is available without charge on our website. In the event that we amend or waive any of the provisions of the Ethics Policy Statement applicable to our Chief Executive Officer or Chief Financial Officer, we intend to disclose the same on our website at www.deltaapparelinc.com.
| |
ITEM 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference from the portions of the definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days following the end of our 2013 fiscal year under the headings “Compensation Discussion and Analysis”, “Compensation Tables,” “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” and “Compensation Committee Report.”
| |
ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information relating to security ownership by certain beneficial owners and management is incorporated herein by reference from the portion of the definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days following the end of our 2013 fiscal year under the heading “Stock Ownership of Principal Shareholders and Management.”
On November 11, 2010, the Delta Apparel, Inc. shareholders approved the Delta Apparel, Inc. 2010 Stock Plan ("2010 Stock Plan"). Upon shareholder approval of the 2010 Stock Plan, no additional awards have been or will be granted under either the Delta Apparel Stock Option Plan ("Option Plan") or the Delta Apparel Incentive Stock Award Plan ("Award Plan"); instead, all stock awards have and will be granted under the 2010 Stock Plan. The aggregate number of shares of common stock that may be delivered under the 2010 Stock Plan is 500,000 plus any shares of common stock subject to outstanding awards under the Option Plan or Award Plan that are subsequently forfeited or terminated for any reason before being exercised. The 2010 Stock Plan limits the number of shares that may be covered by awards to any participant in a given calendar year and also limits the aggregate awards of restricted stock, restricted stock units and performance stock granted in any given calendar year.
Set forth in the table below is certain information about securities issuable under our equity compensation plans as of June 29, 2013.
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Plan Category | | Number of securities to
be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights | | Weighted-average
exercise price of
outstanding options, warrants and rights | | Number of securities
remaining available for
future issuance under equity
compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a)) |
| | (a) | | (b) | | (c) |
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | | 203,110 |
| | $ | 3.31 |
| | 588,661 |
|
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | | 660,500 |
| | $ | 12.44 |
| | — |
|
Total | | 863,610 |
| | $ | 10.29 |
| | 588,661 |
|
For additional information on our stock-based compensation plans, see Note 12 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
| |
ITEM 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference from the portion of the definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days following the end of our 2013 fiscal year under the headings “Related Party Transactions” and "Corporate Governance".
| |
ITEM 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference from the portion of the definitive Proxy Statement to be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days following the end of our 2013 fiscal year under the heading “Proposal No. 3: Ratification of Appointment of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm”.
PART IV
| |
ITEM 15. | EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
(a)(1) and (2) Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedules:
| |
• | Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
| |
• | Consolidated Balance Sheets as of June 29, 2013 and June 30, 2012. |
| |
• | Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended June 29, 2013, June 30, 2012 and July 2, 2011. |
| |
• | Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss) for the years ended June 29, 2013, June 30, 2012 and July 2, 2011. |
| |
• | Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity for the years ended June 29, 2013, June 30, 2012 and July 2, 2011. |
| |
• | Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended June 29, 2013, June 30, 2012 and July 2, 2011. |
| |
• | Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
The following consolidated financial statement schedule of Delta Apparel, Inc. and subsidiaries is included in Item 15(c):
| |
• | Schedule II — Consolidated Valuation and Qualifying Accounts |
All other schedules for which provision is made in the applicable accounting regulation of the Securities and Exchange Commission are not required under the related instructions or are inapplicable, and therefore have been omitted. Columns omitted from schedules filed have been omitted because the information is not applicable.
(a)(3) Listing of Exhibits*
| |
2.1 | Amended and Restated Stock Purchase Agreement dated as of October 3, 2003, among Delta Apparel, Inc., MJS Acquisition Company, M. J. Soffe Co., James F. Soffe, John D. Soffe, and Anthony M. Cimaglia (excluding schedules and exhibits): Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K/A filed on October 17, 2003. |
| |
2.1.1 | First Amendment to Amended and Restated Stock Purchase Agreement dated as of November 10, 2004, among Delta Apparel, Inc., M. J. Soffe Co., James F. Soffe, John D. Soffe, and Anthony M. Cimaglia: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.2.1 to the Company’s Form 10-Q filed on February 9, 2005. |
| |
2.2 | Asset Purchase Agreement dated as of August 22, 2005, among Delta Apparel, Inc., Junkfood Clothing Company, Liquid Blaino Designs, Inc. d/b/a Junkfood Clothing, Natalie Grof, and Blaine Halvorson (excluding schedules and exhibits): Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on August 26, 2005. |
| |
2.3 | Asset Purchase Agreement dated as of August 17, 2006, among Delta Apparel, Inc., Fun-Tees, Inc., Henry T. Howe, James C. Poag, Jr., Beverly H. Poag, Lewis G. Reid, Jr., Kurt R. Rawald, Larry L. Martin, Jr., Julius D. Cline and Marcus F. Weibel: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on August 21, 2006. |
| |
2.4 | Asset Purchase Agreement dated as of November 18, 2004, among Delta Apparel, Inc. and Parkdale America LLC: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.3 to the Company's Form 10-Q filed on February 9, 2005. |
| |
2.4.1 | First Amendment to Asset Purchase Agreement dated as of December 31, 2004, among Delta Apparel, Inc. and Parkdale America LLC: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.3.1 to the Company's Form 10-Q filed on February 9, 2005. |
| |
2.5 | Asset Purchase Agreement dated as of August 27, 2013, among To The Game, LLC, Salt Life Holdings, LLC, Roger L. Combs, Sr., Donald R. Combs, Richard Thompson, and Michael T. Hutto (excluding schedules and exhibits): Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on August 29, 2013. |
| |
3.1.1 | Articles of Incorporation of the Company: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Company’s Form 10-12B filed on December 30, 1999. |
| |
3.1.2 | Amendment to Articles of Incorporation of the Company dated September 18, 2003: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1.2 to the Company’s Form 10-Q filed on November 5, 2003. |
| |
3.1.3 | Amendment to Articles of Incorporation of the Company dated April 28, 2005: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1.3 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on April 29, 2005. |
| |
3.1.4 | Amendment to Articles of Incorporation of the Company dated November 8, 2007: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1.4 to the Company’s Form 10-K filed on August 28, 2009. |
| |
3.2.1 | Bylaws of the Company: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2.1 to the Company’s Form 10-K filed on August 28, 2009. |
| |
3.2.2 | Amendment to Bylaws of the Company adopted January 20, 2000: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2.2 to the Company’s Form 10-K filed on August 28, 2009. |
| |
3.2.3 | Amendment to Bylaws of the Company adopted February 17, 2000: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2.3 to the Company’s Form 10-K filed on August 28, 2009. |
| |
3.2.4 | Amendment to Bylaws of the Company adopted June 6, 2000: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2.4 to the Company’s Form 10-K filed on August 28, 2009. |
| |
3.2.5 | Amendment to Bylaws dated August 17, 2006: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2.5 to the Company’s Form 10-K filed on August 28, 2009. |
| |
3.2.6 | Amendment to Bylaws dated August 12, 2009: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2.6 to the Company’s Form 10-K filed on August 28, 2009. |
| |
4.1 | See Exhibits 3.1.1, 3.1.2, 3.1.3, 3.1.4, 3.2.1, 3.2.2, 3.2.3, 3.2.4, 3.2.5, and 3.2.6. |
| |
4.2 | Specimen certificate for common stock, par value $0.01 per share, of the Company: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Company’s Form 10-12 B/A filed on May 3, 2000. |
| |
10.1 | See Exhibits 2.1, 2.1.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 and 2.4.1. |
| |
10.2 | Fourth Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement, dated May 27, 2011, among Delta Apparel, Inc., M.J. Soffe, LLC (successor by merger to TCX, LLC), Junkfood Clothing Company, To The Game, LLC, and Art Gun, LLC, the financial institutions named therein as Lenders, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Administrative Agent, Bank of America, N.A., as Syndication Agent, Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Sole Lead Arranger, and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC and Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as Joint Bookrunners: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on June 3, 2011. |
| |
10.2.1 | Consent and First Amendment to Fourth Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement, dated August 27, 2013, among Delta Apparel, Inc., M.J. Soffe, LLC (successor by merger to TCX, LLC), Junkfood Clothing Company, To The Game, LLC, and Art Gun, LLC, the financial institutions named therein as Lenders, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Administrative Agent, Bank of America, N.A., as Syndication Agent, Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Sole Lead Arranger, and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC and Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as Joint Bookrunners: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on August 29, 2013. |
| |
10.3 | Delta Apparel, Inc. 2000 Stock Option Plan, Effective as of February 15, 2000, Amended & Restated March 15, 2000: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company’s Form 10-12B/A filed on March 31, 2000.*** |
| |
10.4 | Delta Apparel, Inc. Incentive Stock Award Plan, Effective February 15, 2000, Amended & Restated March 15, 2000: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Company’s Form 10-12B/A filed on March 31, 2000.*** |
| |
10.5 | Delta Apparel, Inc. 2010 Stock Plan: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on November 4, 2010.*** |
| |
10.6 | Yarn Supply Agreement dated as of January 5, 2005, between Delta Apparel, Inc. and Parkdale Mills, LLC and Parkdale America, LLC: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.29 to the Company’s Form 10-Q filed on February 9, 2005.** |
| |
10.6.1 | First Amendment to Yarn Supply Agreement dated as of June 26, 2009 between Delta Apparel, Inc. and Parkdale Mills, LLC, and Parkdale America, LLC.: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7.1 to the Company’s Form 10-K filed on August 28, 2009.** |
| |
10.6.2 | Second Amendment to Yarn Supply Agreement dated as of October 21, 2011 between Delta Apparel, Inc. and Parkdale Mills, LLC, and Parkdale America, LLC.: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on October 25, 2011.** |
| |
10.6.3 | Third Amendment to Yarn Supply Agreement dated as of March 11, 2013, between Delta Apparel, Inc. and Parkdale Mills, LLC, and Parkdale America, LLC.: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on March 14, 2013.** |
| |
10.7 | Employment Agreement between Delta Apparel, Inc. and Deborah H. Merrill dated December 31, 2012: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on January 3, 2013.*** |
| |
10.8 | Employment Agreement between Delta Apparel, Inc. and Martha M. Watson dated December 31, 2012: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on January 3, 2013.*** |
| |
10.9 | Employment Agreement between Delta Apparel, Inc. and Steven E. Cochran dated December 31, 2012: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company's Form 8-K filed on January 3, 2013.*** |
| |
10.9.1 | Amendment to Employment Agreement between Delta Apparel, Inc. and Steven E. Cochran dated January 28, 2013: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on January 29, 2013.*** |
| |
10.11 | Employment Agreement between Delta Apparel, Inc. and Robert W. Humphreys dated June 10, 2009: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to the Company’s Form 10-K filed on August 28, 2009.*** |
| |
10.11.1 | First Amendment to Employment Agreement between Delta Apparel, Inc. and Robert W. Humphreys dated August 17, 2011: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on August 19, 2011.*** |
| |
10.11.2 | Second Amendment to Employment Agreement between Delta Apparel, Inc. and Robert W. Humphreys dated June 6, 2012: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Form 8-K filed on June 8, 2012.*** |
| |
10.12 | Form of Restricted Stock Unit and Performance Unit Award Agreement: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company's Form 10-Q filed on November 3, 2011.*** |
| |
10.13 | Delta Apparel Short-Term Incentive Compensation Plan: Incorporated by reference to Exhibit A of the Company's Proxy Statement filed on September 28, 2011.*** |
| |
10.14 | Form of Restricted Stock Unit and Performance Unit Award Agreement.*** |
| |
21 | Subsidiaries of the Company. |
| |
23.1 | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
| |
31.1 | Certification of the Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
| |
31.2 | Certification of the Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
| |
32.1 | Certification of the Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
| |
32.2 | Certification of the Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. |
______________________
|
| | |
* | | All reports previously filed by the Company with the Commission pursuant to the Securities Exchange Act, and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder, exhibits of which are incorporated to this Report by reference thereto, were filed under Commission File Number 1-15583. |
** | | Portions of this exhibit have been omitted pursuant to a request for confidential treatment and have been filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission. |
*** | | This is a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
The registrant agrees to furnish supplementally to the Securities and Exchange Commission a copy of any omitted schedule or exhibit to any of the above filed exhibits upon request of the Commission.
(b) Exhibits
See Item 15(a)(3) above.
(c) Schedules
See information under (a)(1) and (2) of Item 15.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
| | |
| | DELTA APPAREL, INC. |
| | (Registrant) |
| | |
August 29, 2013 | | By: /s/ Deborah H. Merrill |
Date | | Deborah H. Merrill |
| | Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer |
| | (principal financial and accounting officer) |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and as of the dates indicated.
|
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
/s/ James A. Cochran | 8/27/2013 | | /s/ David Peterson | 8/28/2013 |
James A. Cochran | Date | | David Peterson | Date |
Director | | | Director | |
| | | | |
/s/ Sam P. Cortez | 8/27/2013 | | /s/ Deborah H. Merrill | 8/29/2013 |
Sam P. Cortez | Date | | Deborah H. Merrill | Date |
Director | | | Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and | |
| | | Treasurer (principal financial and accounting officer) |
| | | | |
/s/ Elizabeth J. Gatewood | 8/26/2013 | | /s/ Suzanne B. Rudy | 8/27/2013 |
Elizabeth J. Gatewood | Date | | Suzanne B. Rudy | Date |
Director | | | Director | |
| | | | |
/s/ G. Jay Gogue | 8/27/2013 | | /s/ Robert E. Staton, Sr | 8/27/2013 |
G. Jay Gogue | Date | | Robert E. Staton, Sr. | Date |
Director | | | Director | |
| | | | |
/s/ Robert W. Humphreys | 8/29/2013 | | | |
Robert W. Humphreys | Date | | | |
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer | | | | |
| | | | |
[Page intentionally left blank]
Delta Apparel, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders of Delta Apparel, Inc. and subsidiaries
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Delta Apparel, Inc. and subsidiaries as of June 29, 2013, and June 30, 2012, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, shareholders' equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended June 29, 2013. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15(a). These financial statements and schedule are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of Delta Apparel, Inc. and subsidiaries at June 29, 2013, and June 30, 2012, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended June 29, 2013, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Also, in our opinion, the related financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), Delta Apparel, Inc.'s internal control over financial reporting as of June 29, 2013, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (1992 framework) and our report dated August 29, 2013 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Atlanta, Georgia
August 29, 2013
Delta Apparel, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(Amounts in thousands, except share amounts and per share data)
|
| | | | | | | |
| June 29, 2013 | | June 30, 2012 |
Assets | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 598 |
| | $ | 467 |
|
Accounts receivable, net | 74,415 |
| | 73,349 |
|
Other receivables | 412 |
| | 507 |
|
Income tax receivable | 2,238 |
| | 8,796 |
|
Inventories, net | 159,514 |
| | 161,633 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 4,129 |
| | 3,770 |
|
Deferred income taxes | 4,556 |
| | 4,964 |
|
Total current assets | 245,862 |
| | 253,486 |
|
| | | |
Property, plant and equipment, net | 39,446 |
| | 39,425 |
|
Goodwill | 16,812 |
| | 16,812 |
|
Intangibles, net | 6,190 |
| | 6,797 |
|
Other assets | 3,600 |
| | 3,874 |
|
Total assets | $ | 311,910 |
| | $ | 320,394 |
|
| | | |
Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity | | | |
Liabilities: | | | |
Accounts payable | $ | 50,472 |
| | $ | 46,320 |
|
Accrued expenses | 18,426 |
| | 16,608 |
|
Current portion of long-term debt | 3,529 |
| | 3,529 |
|
Total current liabilities | 72,427 |
| | 66,457 |
|
| | | |
Long-term debt, less current maturities | 94,763 |
| | 110,949 |
|
Deferred income taxes | 3,571 |
| | 3,803 |
|
Other liabilities | 83 |
| | 218 |
|
Total liabilities | $ | 170,844 |
| | $ | 181,427 |
|
| | | |
Commitments and contingencies |
| |
|
| | | |
Shareholders’ equity: | | | |
Preferred stock—$0.01 par value, 2,000,000 shares authorized, none issued and outstanding | — |
| | — |
|
Common stock —$0.01 par value, 15,000,000 shares authorized, 9,646,972 shares issued, and 7,922,784 and 8,424,709 shares outstanding as of June 29, 2013 and June 30, 2012, respectively | 96 |
| | 96 |
|
Additional paid-in capital | 60,598 |
| | 60,367 |
|
Retained earnings | 100,014 |
| | 90,830 |
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (82 | ) | | (129 | ) |
Treasury stock —1,724,188 and 1,222,263 shares as of June 29, 2013 and June 30, 2012, respectively | (19,560 | ) | | (12,197 | ) |
Total shareholders’ equity | 141,066 |
| | 138,967 |
|
Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | 311,910 |
| | $ | 320,394 |
|
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Delta Apparel, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(Amounts in thousands, except per share data)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| June 29, 2013 | | June 30, 2012 | | July 2, 2011 |
Net sales | $ | 490,523 |
| | $ | 489,923 |
| | $ | 475,236 |
|
Cost of goods sold | 381,014 |
| | 406,200 |
| | 359,001 |
|
Gross profit | 109,509 |
| | 83,723 |
| | 116,235 |
|
| | | | | |
Selling, general and administrative expenses | 94,944 |
| | 89,973 |
| | 91,512 |
|
Change in fair value of contingent consideration | — |
| | — |
| | (1,530 | ) |
Goodwill impairment charge | — |
| | — |
| | 612 |
|
Other expense (income), net | 662 |
| | (28 | ) | | 345 |
|
Operating income (loss) | 13,903 |
| | (6,222 | ) | | 25,296 |
|
| | | | | |
Interest expense, net | 3,997 |
| | 4,132 |
| | 2,616 |
|
Earnings (loss) before provision for (benefit from) income taxes | 9,906 |
| | (10,354 | ) | | 22,680 |
|
Provision for (benefit from) income taxes | 722 |
| | (7,907 | ) | | 5,353 |
|
Net earnings (loss) | $ | 9,184 |
| | $ | (2,447 | ) | | $ | 17,327 |
|
| | | | | |
Basic earnings (loss) per share | $ | 1.12 |
| | $ | (0.29 | ) | | $ | 2.04 |
|
Diluted earnings (loss) per share | $ | 1.08 |
| | $ | (0.29 | ) | | $ | 1.98 |
|
| | | | | |
Weighted average number of shares outstanding | 8,234 |
| | 8,453 |
| | 8,486 |
|
Dilutive effect of stock options and awards | 252 |
| | — |
| | 261 |
|
Weighted average number of shares assuming dilution | 8,486 |
| | 8,453 |
| | 8,747 |
|
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Delta Apparel, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(Amounts in thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| June 29,
2013 | | June 30,
2012 | | July 2,
2011 |
Net earnings (loss) | $ | 9,184 |
| | $ | (2,447 | ) | | $ | 17,327 |
|
Other comprehensive income (loss) related to unrealized gain (loss) on derivatives | 47 |
| | (115 | ) | | 91 |
|
Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 9,231 |
| | $ | (2,562 | ) | | $ | 17,418 |
|
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Delta Apparel, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity
(Amounts in thousands, except share amounts)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Accumulated | | | | |
| | | | | Additional | | | | Other | | | | |
| Common Stock | | Paid-In | | Retained | | Comprehensive | | Treasury Stock | | |
| Shares | | Amount | | Capital | | Earnings | | Income (Loss) | | Shares | | Amount | | Total |
Balance at July 3, 2010 | 9,646,972 |
| | $ | 96 |
| | $ | 59,111 |
| | $ | 75,950 |
| | $ | (105 | ) | | 1,130,679 |
| | $ | (9,338 | ) | | $ | 125,714 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net earnings and other comprehensive income | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 17,327 |
| | 91 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 17,418 |
|
Stock grant | — |
| | — |
| | 40 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (7,000 | ) | | 58 |
| | 98 |
|
Stock options exercised | — |
| | — |
| | (541 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (75,326 | ) | | 643 |
| | 102 |
|
Excess tax benefits from option exercises | — |
| | — |
| | 84 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 84 |
|
Purchase of common stock | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 176,756 |
| | (2,507 | ) | | (2,507 | ) |
Employee stock based compensation | — |
| | — |
| | 1,056 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,056 |
|
Balance at July 2, 2011 | 9,646,972 |
| | 96 |
| | 59,750 |
| | 93,277 |
| | (14 | ) | | 1,225,109 |
| | (11,144 | ) | | 141,965 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss and other comprehensive loss | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (2,447 | ) | | (115 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (2,562 | ) |
Stock grant | — |
| | — |
| | (83 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (9,000 | ) | | 83 |
| | — |
|
Stock options exercised | — |
| | — |
| | (1,559 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (161,966 | ) | | 1,506 |
| | (53 | ) |
Excess tax benefits from option exercises | — |
| | — |
| | 529 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 529 |
|
Purchase of common stock | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 168,120 |
| | (2,642 | ) | | (2,642 | ) |
Employee stock based compensation | — |
| | — |
| | 1,730 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,730 |
|
Balance at June 30, 2012 | 9,646,972 |
| | 96 |
| | 60,367 |
| | 90,830 |
| | (129 | ) | | 1,222,263 |
| | (12,197 | ) | | 138,967 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net earnings and other comprehensive income | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,184 |
| | 47 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9,231 |
|
Stock grant | — |
| | — |
| | (115 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (11,250 | ) | | 115 |
| | — |
|
Stock options exercised | — |
| | — |
| | (553 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (31,401 | ) | | 339 |
| | (214 | ) |
Excess tax benefits from option exercises | — |
| | — |
| | 34 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 34 |
|
Purchase of common stock | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 544,576 |
| | (7,817 | ) | | (7,817 | ) |
Employee stock based compensation | — |
| | — |
| | 865 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 865 |
|
Balance at June 29, 2013 | 9,646,972 |
| | $ | 96 |
| | $ | 60,598 |
| | $ | 100,014 |
| | $ | (82 | ) | | 1,724,188 |
| | $ | (19,560 | ) | | $ | 141,066 |
|
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Delta Apparel, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(Amounts in thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended |
| June 29, 2013 | | June 30, 2012 | | July 2, 2011 |
Operating activities: | | | | | |
Net earnings (loss) from continuing operations | $ | 9,184 |
| | $ | (2,447 | ) | | $ | 17,327 |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net earnings (loss) to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: | | | | | |
Depreciation | 7,407 |
| | 6,884 |
| | 6,644 |
|
Amortization of intangibles | 607 |
| | 608 |
| | 613 |
|
Amortization of deferred financing fees | 363 |
| | 361 |
| | 313 |
|
Excess tax benefits from exercise of stock options | (34 | ) | | (529 | ) | | (84 | ) |
Provision for (benefit from) deferred income taxes | 176 |
| | (1,107 | ) | | 1,282 |
|
(Benefit from) provision for allowances on accounts receivable, net | (513 | ) | | 530 |
| | (354 | ) |
Non-cash stock compensation | 865 |
| | 1,730 |
| | 1,056 |
|
Change in the fair value of contingent consideration | — |
| | — |
| | (1,530 | ) |
Goodwill impairment charge | — |
| | — |
| | 612 |
|
Loss on disposal of property and equipment | 93 |
| | 73 |
| | 111 |
|
Fixed asset impairment charge | 328 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Inventory write down | — |
| | 16,195 |
| | — |
|
Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of effect of acquisitions: | | | | | |
Accounts receivable | (458 | ) | | 2,435 |
| | (11,673 | ) |
Inventories | 2,119 |
| | (18,619 | ) | | (36,441 | ) |
Prepaid expenses and other current assets | (358 | ) | | 289 |
| | (411 | ) |
Other non-current assets | (90 | ) | | (19 | ) | | 125 |
|
Accounts payable | 4,152 |
| | (9,234 | ) | | 20,897 |
|
Accrued expenses | 1,818 |
| | (7,099 | ) | | 4,109 |
|
Income taxes | 6,592 |
| | (9,236 | ) | | 341 |
|
Other liabilities | (88 | ) | | 84 |
| | (47 | ) |
Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities | 32,163 |
| | (19,101 | ) | | 2,890 |
|
| | | | | |
Investing activities: | | | | | |
Purchases of property and equipment | (7,922 | ) | | (6,626 | ) | | (7,966 | ) |
Proceeds from sale of equipment | 72 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Cash paid for businesses, net of cash acquired | — |
| | — |
| | (9,884 | ) |
Net cash used in investing activities | (7,850 | ) | | (6,626 | ) | | (17,850 | ) |
| | | | | |
Financing activities: | | | | | |
Proceeds from long-term debt | 486,908 |
| | 544,295 |
| | 511,358 |
|
Repayment of long-term debt | (503,094 | ) | | (516,590 | ) | | (492,658 | ) |
Payment of financing fees | — |
| | — |
| | (1,450 | ) |
Repurchase of common stock | (7,817 | ) | | (2,642 | ) | | (2,507 | ) |
Proceeds from exercise of stock options | 23 |
| | 18 |
| | 263 |
|
Payment of withholding taxes on exercise of stock options | (236 | ) | | (72 | ) | | (161 | ) |
Excess tax benefits from exercise of stock options | 34 |
| | 529 |
| | 84 |
|
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (24,182 | ) | | 25,538 |
| | 14,929 |
|
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | 131 |
| | (189 | ) | | (31 | ) |
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 467 |
| | 656 |
| | 687 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 598 |
| | $ | 467 |
| | $ | 656 |
|
| | | | | |
Supplemental cash flow information: | | | | | |
Cash paid during the year for interest | $ | 3,458 |
| | $ | 3,532 |
| | $ | 2,229 |
|
Cash (received) paid during the year for income taxes, net of refunds received | $ | (6,013 | ) | | $ | 2,370 |
| | $ | 3,922 |
|
Non-cash financing activity—issuance of common stock | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 98 |
|
See accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Delta Apparel, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
June 29, 2013
NOTE 1—THE COMPANY
Delta Apparel, Inc. is an international apparel design, marketing, manufacturing and sourcing company that features a diverse portfolio of lifestyle basics and branded activewear apparel and headwear. We specialize in selling casual and athletic products through a variety of distribution channels and distribution tiers, including specialty stores, boutiques, department stores, mid and mass channels, college bookstores and the U.S. military. Our products are made available direct-to-consumer on our websites at www.soffe.com, www.junkfoodclothing.com, www.saltlife.com and www.deltaapparel.com. We design and internally manufacture the majority of our products, which allows us to offer a high degree of consistency and quality controls as well as leverage scale efficiencies. We have manufacturing operations located in the United States, El Salvador, Honduras and Mexico, and use domestic and foreign contractors as additional sources of production. Our distribution facilities are strategically located throughout the United States to better serve our customers with same-day shipping on our catalog products and weekly replenishments to retailers.
NOTE 2—SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
(a) Basis of Presentation: Our consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Delta Apparel and its wholly-owned domestic and foreign subsidiaries. All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. We apply the equity method of accounting for investments in companies where we have less than a 50% ownership interest and over which we exert significant influence. We do not exercise control over these companies and do not have substantive participating rights. As such, these are not considered variable interest entities.
We operate our business in two distinct segments: branded and basics. Although the two segments are similar in their production processes and regulatory environments, they are distinct in their economic characteristics, products, marketing and distribution methods.
(b) Fiscal Year: We operate on a 52-53 week fiscal year ending on the Saturday closest to June 30. The 2013, 2012 and 2011 fiscal years were 52-week years and ended on June 29, 2013, June 30, 2012 and July 2, 2011, respectively.
(c) Use of Estimates: The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make certain estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts and disclosures of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Estimates are adjusted to reflect actual experience when necessary. Significant estimates and assumptions affect many items in our financial statements, for example: allowance for doubtful trade receivables, sales returns and allowances, inventory obsolescence, the carrying value of goodwill, and income tax assets and related valuation allowance. Our actual results may differ from our estimates.
(d) Revenue Recognition: Revenues from product sales are recognized when ownership is transfered to the customer, which includes not only the passage of title, but also the transfer of the risk of loss related to the product. At this point, the sales price is fixed and determinable, and we are reasonably assured of the collectibility of the sale. The majority of our sales are shipped FOB shipping point and revenue is therefore recognized when the goods are shipped to the customer. For sales that are shipped FOB destination point, we do not recognize the revenue until the goods are received by the customer. Shipping and handling charges billed to our customers are included in net revenue and the related costs are included in cost of goods sold. Revenues are reported on net sales basis, which is computed by deducting product returns, discounts and estimated returns and allowances. We estimate returns and allowances on an ongoing basis by considering historical and current trends.
Royalty revenue is primarily derived from royalties paid to us by licensees of our intellectual property rights, which include, among other things, trademarks and copyrights. We execute license agreements with our licensees detailing the terms of the licensing arrangement. Royalties are generally recognized upon receipt of the licensees' royalty report, in accordance with the terms of the executed license agreement, and when all other revenue recognition criteria have been met.
(e) Sales Tax: Sales tax collected from customers and remitted to various government agencies are presented on a net basis (excluded from revenues) in the Consolidated Statements of Operations.
(f) Cash and Cash Equivalents: Cash and cash equivalents consists of cash and temporary investments with original maturities of three months or less.
(g) Accounts Receivable: Accounts receivable consists primarily of receivables from our customers arising from the sale of our products, and we generally do not require collateral from our customers. We actively monitor our exposure to credit risk through the use of credit approvals and credit limits. At June 29, 2013, our net accounts receivable was $74.4 million, consisting of $76.2 million in accounts receivable and $1.8 million in reserves. At June 30, 2012, our net accounts receivable was $73.3 million, consisting of $75.6 million in accounts receivable and $2.3 million in reserves.
We estimate the net collectibility of our accounts receivable and establish an allowance for doubtful accounts based upon this assessment. In situations where we are aware of a specific customer’s inability to meet its financial obligation, such as in the case of a bankruptcy
filing, a specific reserve for bad debts is recorded against amounts due to reduce the net recognized receivable to the amount reasonably expected to be collected. For all other customers, reserves are determined through analysis of the aging of accounts receivable balances, historical bad debts, customer concentrations, customer credit-worthiness, current economic trends and changes in customer payment terms. In addition, reserves are established for other concessions that have been extended to customers, including advertising, markdowns and other accommodations, net of historical recoveries. These reserves are determined based upon historical deduction trends and evaluation of current market conditions. Bad debt expense was less than 0.1%, 0.1% and 0.1%, of net sales in 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
(h) Inventories: We state inventories at the lower of cost or market using the first-in, first-out method. Inventory cost includes materials, labor and manufacturing overhead on manufactured inventory, and all direct and associated costs, including inbound freight, to acquire sourced products. We regularly review inventory quantities on hand and record reserves for obsolescence, excess quantities, irregulars and slow moving inventory based on historical selling prices, current market conditions, and forecasted product demand to reduce inventory to its net realizable value. See Note 2(x) for further information regarding yarn procurements.
During the second quarter of fiscal year 2012, we recorded a $16.2 million lower of cost or market write-down on the inventory in the basics segment and its firm purchase commitments for yarn resulting from historically high cotton prices in its inventory costs combined with declining selling prices. The estimation of the total write-down involved management judgments and assumptions including assumptions regarding future selling price forecasts, the allocation of raw materials between business units, the estimated costs to complete, disposal costs and a normal profit margin. The inventory and yarn firm purchase commitments associated with this inventory write-down was sold during our fiscal year 2012.
(i) Property, Plant and Equipment: Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost. We depreciate and amortize our assets on a straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, which range from three to twenty-five years. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of the lease term or the estimated useful life of the improvements. Assets that we acquire under non-cancelable leases that meet the criteria of capital leases are capitalized in property, plant and equipment and amortized over the useful lives of the related assets. When we retire or dispose of assets, the costs and accumulated depreciation or amortization are removed from the respective accounts and we recognize any related gain or loss. Repairs and maintenance costs are charged to expense when incurred. Major replacements that substantially extend the useful life of an asset are capitalized and depreciated.
(j) Internally Developed Software Costs. We account for internally developed software in accordance with FASB Codification No. 350-40, Intangibles-Goodwill and Other, Internal-Use Software. After technical feasibility has been established, we capitalize the cost of our software development process, including payroll and payroll benefits, by tracking the software development hours invested in the software projects. We amortize our software development costs in accordance with the estimated economic life of the software, which is generally three to ten years.
(k) Impairment of Long-Lived Assets (Including Amortizable Intangible Assets): In accordance with FASB Codification No. 360, Property, Plant, and Equipment, our long-lived assets are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the assets may not be recoverable. When evaluating assets for potential impairment, we compare the carrying amount of the asset to the undiscounted future net cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If impairment is indicated, the asset is permanently written down to its estimated fair market value (based upon future discounted cash flows) and an impairment loss is recognized.
During the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2013, the decision was made to consolidate our domestic screen print operations, resulting in the closure of the Wendell, North Carolina decorating facility. Due to the expected closure, we performed an impairment analysis which resulted in a $0.3 million impairment that we recorded in the other income (expense) line item in our Consolidated Statements of Operations.
(l) Goodwill and Intangibles: We recorded goodwill and intangibles with definite lives, including trade names and trademarks, customer relationships, technology, and non-compete agreements, in conjunction with the acquisitions of Junkfood Clothing Company and Art Gun. Intangible assets are amortized based on their estimated economic lives, ranging from four to twenty years. Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of net identified tangible and intangible assets and liabilities acquired, and is not amortized. The total amount of goodwill is expected to be deductible for tax purposes. See Note 6 — Goodwill and Intangible Assets for further details.
(m) Impairment of Goodwill: We evaluate the carrying value of goodwill annually or more frequently if events or circumstances indicate that an impairment loss may have occurred. Such circumstances could include, but are not limited to, a significant adverse change in business climate, increased competition or other economic conditions. Under FASB Codification No. 350, Intangibles — Goodwill and Other ("ASC 350"), goodwill is tested at a reporting unit level. As of the beginning of fiscal year 2012, Junkfood was the only reporting unit with recorded goodwill.
The Company adopted ASU No. 2011-08, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other (Topic 350), Testing for Goodwill Impairment ("ASU 2011-08") on July 1, 2012. ASU 2011-08 simplifies how companies are required to test goodwill for impairment. Companies now have the option to first assess qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not (likelihood of more than 50%) that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If after considering the totality of events and circumstances a company determines
it is not more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, it will not have to perform the two-step impairment test.
If the company determines that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, or it chooses to not take the simplified approach, the company will have to perform the two-step impairment test. The first step involves comparing the fair value of the reporting unit to which the goodwill is assigned to its carrying amount. If this comparison indicates that a reporting unit’s estimated fair value is less than its carrying value, a second step is required. If applicable, the second step requires a company to allocate the estimated fair value of the reporting unit to the estimated fair value of the reporting unit’s net assets, with any fair value in excess of amounts allocated to such net assets representing the implied fair value of goodwill for that reporting unit. If the carrying value of the goodwill exceeds its implied fair value, the carrying value is written down by an amount equal to such excess.
We complete our annual impairment test of goodwill on the first day of our third fiscal quarter. We estimate fair value of the applicable reporting unit or units using a discounted cash flow methodology. This represents a level 3 fair value measurement as defined under ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures, since the inputs are not readily observable in the marketplace. The goodwill impairment testing process involves the use of significant assumptions, estimates and judgments with respect to a variety of factors, including sales, gross margins, selling, general and administrative expenses, capital expenditures, cash flows and the selection of an appropriate discount rate, all of which are subject to inherent uncertainties and subjectivity. When we perform goodwill impairment testing, our assumptions are based on annual business plans and other forecasted results, which we believe represent those of a market participant. We select a discount rate, which is used to reflect market-based estimates of the risks associated with the projected cash flows, based on the best information available as of the date of the impairment assessment. Based on the valuation, there is not an impairment on the goodwill associated with Junkfood, the only goodwill recorded on our financial statements.
At the end of each reporting period, we are required to remeasure the fair value of the contingent consideration related to the Art Gun acquisition in accordance with FASB Codification No. 805, Business Combinations (“ASC 805”). Based on the operating results and projections for Art Gun, we analyzed and concluded that the fair value of the contingent consideration was de minimis, resulting in a $1.5 million favorable adjustment recorded in the second fiscal quarter of 2011. The change in fair value of the contingent consideration created an indicator of impairment for the goodwill associated with Art Gun. In accordance with ASC 350, we performed an interim impairment test of goodwill as of the end of the second quarter of fiscal year 2011. Under the first step of the impairment analysis for Art Gun, we considered both the income approach, which estimates the fair value based on the future discounted cash flows, and the market approach, which estimates the fair value based on comparable market prices, both of which fall in level 3 of the fair value hierarchy. The results of step one of the impairment test indicated that the carrying value of the Art Gun reporting unit exceeded its fair value. The second step of the impairment test required us to allocate the estimated fair value of Art Gun to the estimated fair value of Art Gun's net assets, with any fair value in excess of amounts allocated to such net assets representing the implied fair value of goodwill. The result indicated that the goodwill at Art Gun was fully impaired, resulting in a $0.6 million impairment charge recorded in the second quarter of fiscal 2011. The change in contingent consideration and goodwill impairment charge resulted in a net favorable adjustment of $0.9 million, which is included in the branded segment in fiscal year 2011. At June 29, 2013, the fair value of the contingent consideration was remeasured based on Art Gun's historical and current operating results and projections, remained de minimis, and no amounts are expected to be paid under the terms of the arrangements.
Given the current macro-economic environment and the uncertainties regarding its potential impact on our business, there can be no assurance that our estimates and assumptions used in our impairment tests will prove to be accurate predictions of the future. If our assumptions regarding forecasted cash flows are not achieved, it is possible that an impairment review may be triggered and goodwill may be determined to be impaired.
(n) Self-Insurance Reserves: Our medical, prescription and dental care benefits are primarily self-insured. Our self-insurance accruals are based on claims filed and estimates of claims incurred but not reported. We develop estimates of claims incurred but not reported based upon the historical time it takes for a claim to be reported and paid and historical claim amounts. We had self-insurance reserves of approximately $0.5 million and $0.7 million at June 29, 2013 and June 30, 2012, respectively.
(o) Income Taxes: We account for income taxes under the liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases, and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
(p) Cost of Goods Sold: We include in cost of goods sold all manufacturing and sourcing costs incurred prior to the receipt of finished goods at our distribution facilities. The cost of goods sold principally includes product cost, purchasing costs, inbound freight charges, insurance, and inventory write-downs. Our gross margins may not be comparable to other companies, since some entities include costs related to their distribution network in cost of goods sold and we exclude them from gross margin, including them instead in selling, general and administrative expenses.
(q) Selling, General and Administrative Expense: We include in selling, general and administrative expenses costs incurred subsequent to the receipt of finished goods at our distribution facilities, such as the cost of stocking, warehousing, picking and packing, and shipping
goods for delivery to our customers. Distribution costs included in selling, general and administrative expenses totaled $17.5 million, $16.4 million and $14.3 million in fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. In addition, selling, general and administrative expenses include costs related to sales associates, administrative personnel cost, advertising and marketing expenses, royalty payments on licensed products, and other general and administrative expenses.
(r) Advertising Costs: All costs associated with advertising and promoting our products are expensed during the year in which they are incurred and are included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. We participate in cooperative advertising programs with our customers. Depending on the customer, our defined cooperative programs allow the customer to use from 1% to 5% of its net purchases from us towards advertisements of our products. Because our products are being specifically advertised, we are receiving an identifiable benefit resulting from the consideration for cooperative advertising. Therefore, pursuant to FASB Codification No. 605-50, Revenue Recognition, Customers Payments and Incentives, we record cooperative advertising costs as a selling expense and the related cooperative advertising reserve as an accrued liability. Advertising costs totaled $3.8 million, $4.3 million and $6.7 million in fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. Included in these costs were $1.5 million, $2.0 million and $1.9 million in fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively, related to our cooperative advertising programs.
(s) Stock-Based Compensation: Stock-based compensation cost is accounted for under the provisions of FASB Codification No. 718, Compensation – Stock Compensation (“ASC 718”), the Securities and Exchange Commission Staff Accounting bulletin No. 107 ("SAB 107"), and the Securities and Exchange Commission Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 110 ("SAB 110"). ASC 718 requires all stock-based payments to employees, including grants of employee stock options, to be recognized as expense over the vesting period using a fair value method. We estimate the fair value of stock options using the Black-Scholes options pricing model. The fair value of our restricted stock awards is the quoted market value of Delta Apparel's stock on the grant date. For performance-based stock awards, in the event we determine it is no longer probable that we will achieve the minimum performance criteria specified in the award, we reverse all of the previously recognized compensation expense in the period such a determination is made. We recognize the fair value, net of estimated forfeitures, as a component of cost of sales and selling, general and administrative expense in the Consolidated Statements of Operations over the vesting period.
(t) Earnings per Share: We compute basic earnings per share ("EPS") by dividing net income by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the year pursuant to FASB Codification No. 260, Earnings Per Share (“ASC 260”). Basic EPS includes no dilution. Diluted EPS is calculated, as set forth in ASC 260, by dividing net income by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding adjusted for the issuance of potentially dilutive shares. Potential dilutive shares consist of common stock issuable under the assumed exercise of outstanding stock options and awards using the treasury stock method. This method, as required by ASC 718, assumes that the potential common shares are issued and the proceeds from the exercise, along with the amount of compensation expense attributable to future services, are used to purchase common stock at the exercise date. The difference between the number of potential shares issued and the number of shares purchased is added as incremental shares to the actual number of shares outstanding to compute diluted EPS. Outstanding stock options and awards that result in lower potential shares issued than shares purchased under the treasury stock method are not included in the computation of diluted EPS since their inclusion would have an anti-dilutive effect on EPS.
(u) Foreign Currency Translation: Our functional currency for our foreign operated manufacturing facilities is the United States dollar. We remeasure those assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies using exchange rates in effect at each balance sheet date. Fixed assets and the related accumulated depreciation or amortization are recorded at the exchange rates in effect on the date we acquired the assets. Revenues and expenses denominated in foreign currencies are remeasured using average exchange rates for all periods presented. We recognize the resulting foreign exchange gains and losses as a component of other income and expense in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. These gains and losses are immaterial for all periods presented.
(v) Fair Value of Financial Instruments: We use financial instruments in the normal course of our business. The carrying values approximate fair values for financial instruments that are short-term in nature, such as cash, accounts receivable and accounts payable. We estimate that the carrying value of our long-term debt approximates fair value based on the current rates offered to us for debt of the same remaining maturities.
(w) Other Comprehensive Income (Loss): Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) consists of net earnings and unrealized gains (losses) from cash flow hedges, net of tax, and is presented in the Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity. Accumulated other comprehensive loss contained in the shareholders’ equity section of the Consolidated Balance Sheets in fiscal years 2013 and 2012 consisted of $82 thousand and $129 thousand, respectively, related to interest rate swap agreements.
(x) Yarn and Cotton Procurements: We have a supply agreement with Parkdale to supply our yarn requirements until December 31, 2015. Under the supply agreement, we purchase from Parkdale all of our yarn requirements for use in our manufacturing operations, excluding yarns that Parkdale does not manufacture or cannot manufacture due to temporary capacity constraints. The purchase price of yarn is based upon the cost of cotton plus a fixed conversion cost. Thus, we are subject to the commodity risk of cotton prices and cotton price movements, which could result in unfavorable yarn pricing for us. We fix the cotton prices as a component of the purchase price of yarn, pursuant to the supply agreement, in advance of the shipment of finished yarn from Parkdale. Prices are set according to prevailing prices, as reported by the New York Cotton Exchange, at the time we elect to fix specific cotton prices.
(y) Derivatives: From time to time we enter into forward contracts, option agreements or other instruments to limit our exposure to fluctuations in interest rates and raw material prices with respect to long-term debt and cotton purchases, respectively. We determine at inception whether the derivative instruments will be accounted for as hedges.
We account for derivatives and hedging activities in accordance with FASB Codification No. 815, Derivatives and Hedging (“ASC 815”), as amended. ASC 815 establishes accounting and reporting standards for derivative instruments, including certain derivative instruments embedded in other contracts and hedging activities. It requires the recognition of all derivative instruments as either assets or liabilities in the Consolidated Balance Sheets and measurement of those instruments at fair value. The accounting treatment of changes in fair value depends upon whether or not a derivative instrument is designated as a hedge and, if so, the type of hedge. We include all derivative instruments at fair value in our Consolidated Balance Sheets. For derivative financial instruments related to the production of our products that are not designated as a hedge, we recognize the changes in fair value in cost of sales. For derivatives designated as cash flow hedges, to the extent effective, we recognize the changes in fair value in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) until the hedged item is recognized in income. Any ineffectiveness in the hedge is recognized immediately in income in the line item that is consistent with the nature of the hedged risk. We formally document all relationships between hedging instruments and hedged items, as well as risk management objectives and strategies for undertaking various hedge transactions, at the inception of the transactions.
We are exposed to counterparty credit risks on all derivatives. Because these amounts are recorded at fair value, the full amount of our exposure is the carrying value of these instruments. We only enter into derivative transactions with well established institutions and therefore we believe the counterparty credit risk is minimal.
There were no significant raw material option agreements that were purchased during fiscal year 2013, 2012 or 2011. On September 1, 2011, we entered into three interest rate swap agreements, as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| Effective Date | | Notational Amount | | LIBOR Rate | | Maturity Date |
Interest Rate Swap | 9/1/2011 | | $10 million | | 0.7650 | % | | 9/1/2013 |
Interest Rate Swap | 9/1/2011 | | $10 million | | 0.9025 | % | | 3/1/2014 |
Interest Rate Swap | 9/1/2011 | | $10 million | | 1.0700 | % | | 9/1/2014 |
We assessed these agreements and concluded that the swap agreements match the exact terms of the underlying debt except for a slight timing difference. We use a hypothetical derivative method to assess and measure ineffectiveness associated with the hedge each reporting period. During fiscal years 2013 and 2012, the interest rate swap agreements had minimal ineffectiveness and were considered highly-effective hedges.
The changes in fair value of the interest rate swap agreements resulted in an AOCI gain, net of taxes, of $47 thousand for the year ended June 29, 2013 and an AOCI loss, net of taxes, of $0.1 million the year ended June 30, 2012. See Note 15(d) - Derivatives for further details.
(z) Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements:
In June 2011, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2011-05, Comprehensive Income (Topic 220) - Presentation of Comprehensive Income ("ASU 2011-05"). This new guidance gives companies two choices on how to present items of net income, items of other comprehensive income and total comprehensive income: companies can create one continuous statement of comprehensive income or two separate consecutive statements. Other comprehensive income will no longer be allowed to be presented solely in the statement of stockholders' equity. Earnings per share continues to be based on net income. ASU 2011-05 is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2011 and applied on a retrospective basis. ASU 2011-05 was adopted on July 1, 2012, and the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss) herein comply with this guidance.
In December 2011, the FASB issued ASU 2011-12, Deferral of the Effective Date for Amendments to the Presentation of Reclassifications of Items Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income in Accounting Standards Update No. 2011-05 ("ASU 2011-12"). ASU 2011-12 indefinitely defers the new provisions under ASU 2011-05, which required entities to present reclassification adjustments out of accumulated other comprehensive income by component in both the statement in which net income is presented and the statement in which other comprehensive income is presented for both interim and annual financial statements. ASU 2011-12 is effective for the years beginning after December 15, 2011. ASU 2011-12 was adopted on July 1, 2012, and the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss) herein comply with this guidance.
In September 2011, the FASB issued ASU No. 2011-08, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other (Topic 350), Testing Goodwill for Impairment ("ASU 2011-08") . The FASB decided to simplify how companies are required to test goodwill for impairment. Companies now have the option to first assess qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not (likelihood of more than 50%) that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If after considering the totality of events and circumstances a company determines it is not more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, it will not have to perform the two-step impairment test. The amendments are effective for annual and interim goodwill impairment tests performed for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2011. ASU 2011-08 was adopted on July 1, 2012, and did not have a material effect on our financial statements.
(aa) Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements Not Yet Adopted:
In July 2012, FASB issued ASU No. 2012-02, Intangibles - Goodwill and Other (Topic 350), Testing Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets for Impairment, ("ASU 2012-02"). This new guidance adds an optional qualitative assessment for determining whether an indefinite-lived intangible asset is impaired. Companies have the option to first perform a qualitative assessment to determine whether it is more likely than not (likelihood of more than 50%) that an indefinite-lived intangible is impaired. If a company determines that it is more likely than not that the fair value of such an asset exceeds its carrying amount, it would not need to calculate whether the fair value of such an asset exceeds its carrying amount and it would not need to calculate the fair value of the asset in that year. The company must, however, make a positive assertion about the conclusion and the circumstances taken into account to reach that conclusion. However, if the company determines otherwise, it must calculate the fair value of the asset and compare that value with its carrying amount. If the carrying amount of the company's intangible asset exceeds its fair value, the company must record an impairment charge for the amount of that excess, if any. ASU 2011-02 is effective for annual and interim impairment tests performed for fiscal years beginning after September 15, 2012. Early adoption is permitted. ASU 2012-02 is therefore effective for our fiscal year 2014.
In February 2013, FASB issued ASU No. 2013-02, Comprehensive Income (Topic 220), Reporting of Amounts Reclassified Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (ASU 2013-02). This guidance requires companies to report information about reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive income in one place. These reclassifications must be presented by component. If these items are significant and are reclassified in their entirety in the period, companies must report the effect of the reclassifications on the respective line items in the statement where net income is presented. If the items are not reclassified in their entirety to net income in the period, companies must cross-reference in a note. ASU 2013-02 is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2012. ASU 2013-02 is therefore effective for our fiscal year 2014.
NOTE 3—ACQUISITIONS
On June 11, 2010, we formed a new North Carolina limited liability company, TCX, LLC ("TCX") as a wholly-owned subsidiary of M.J. Soffe, LLC. Pursuant to an Asset Purchase Agreement dated July 5, 2010, on July 12, 2010, TCX acquired substantially all of the net assets of HPM Apparel, Inc. d/b/a The Cotton Exchange, including accounts receivable, inventory, and fixed assets, and assumed certain liabilities. The total purchase price, which included a post-closing working capital adjustment, was $9.9 million. We accounted for the acquisition of The Cotton Exchange pursuant to ASC 805 with the purchase price being allocated based upon fair values. We determined fair values using one or more of the following valuation techniques, all of which are considered level 2 inputs based on the fair value hierarchy: (a) market approach using prices and other relevant information generated by market transactions involving identical or comparable assets or liabilities; or (b) cost approach using amounts that would be required to replace the service capacity of an asset. No goodwill or other intangible assets were recorded in conjunction with the acquisition of The Cotton Exchange. We financed the acquisition completed in fiscal years 2011 using our U.S. asset-based secured credit facility. The acquisition is included in the Consolidated Financial Statements in our branded segment since the acquisition date. Effective January 1, 2012, TCX was merged into its parent entity, M.J. Soffe, LLC, for reasons of corporate simplification and as such, TCX no longer exists as a separate entity.
NOTE 4—INVENTORIES
Inventories, net of reserves of $6.8 million and $5.2 million in fiscal years 2013 and 2012, respectively, consist of the following (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | |
| June 29,
2013 | | June 30,
2012 |
Raw materials | $ | 12,443 |
| | $ | 11,759 |
|
Work in process | 16,407 |
| | 18,986 |
|
Finished goods | 130,664 |
| | 130,888 |
|
| $ | 159,514 |
| | $ | 161,633 |
|
Raw materials include finished yarn and direct materials for the basics segment and include direct embellishment materials and undecorated garments and headwear for the branded segment.
NOTE 5—PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT
Property, plant and equipment consist of the following (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| Estimated Useful Life | | June 29,
2013 | | June 30,
2012 |
Land and land improvements | 25 years | | $ | 993 |
| | $ | 993 |
|
Buildings | 20 years | | 7,882 |
| | 7,893 |
|
Machinery and equipment | 10 years | | 69,094 |
| | 65,404 |
|
Computers and software | 3-10 years | | 20,386 |
| | 19,256 |
|
Furniture and fixtures | 7 years | | 5,290 |
| | 4,973 |
|
Leasehold improvements | 3-10 years | | 2,335 |
| | 2,626 |
|
Automobiles | 5 years | | 797 |
| | 752 |
|
Construction in progress | N/A | | 2,430 |
| | 2,053 |
|
| | | 109,207 |
| | 103,950 |
|
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | | | (69,761 | ) | | (64,525 | ) |
| | | $ | 39,446 |
| | $ | 39,425 |
|
NOTE 6—GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Components of intangible assets consist of the following (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| June 29, 2013 | | June 30, 2012 | | |
| Cost | Accumulated Amortization | Net Value | | Cost | Accumulated Amortization | Net Value | | Economic Life |
| | | | | | | | | |
Goodwill | $ | 16,812 |
| $ | — |
| $ | 16,812 |
| | $ | 16,812 |
| $ | — |
| $ | 16,812 |
| | N/A |
| | | | | | | | | |
Intangibles: | | | | | | | | | |
Tradename/trademarks | $ | 1,530 |
| $ | (603 | ) | $ | 927 |
| | $ | 1,530 |
| $ | (526 | ) | $ | 1,004 |
| | 20 yrs |
Customer relationships | 7,220 |
| (2,847 | ) | 4,373 |
| | 7,220 |
| (2,486 | ) | 4,734 |
| | 20 yrs |
Technology | 1,220 |
| (428 | ) | 792 |
| | 1,220 |
| (307 | ) | 913 |
| | 10 yrs |
Non-compete agreements | 517 |
| (419 | ) | 98 |
| | 517 |
| (371 | ) | 146 |
| | 4 – 8.5 yrs |
Total intangibles | $ | 10,487 |
| $ | (4,297 | ) | $ | 6,190 |
| | $ | 10,487 |
| $ | (3,690 | ) | $ | 6,797 |
| | |
The goodwill cost represents the acquired goodwill net of the cumulative impairment losses of $0.6 million. Amortization expense for intangible assets was $0.6 million for each of the years ended June 29, 2013, June 30, 2012 and July 2, 2011. Amortization expense is estimated to be approximately $0.6 million each for fiscal years 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017 and 2018.
NOTE 7—ACCRUED EXPENSES
Accrued expenses consist of the following (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | |
| June 29,
2013 | | June 30,
2012 |
Accrued employee compensation and benefits | $ | 9,762 |
| | $ | 7,645 |
|
Taxes accrued and withheld | 1,199 |
| | 1,133 |
|
Accrued insurance | 568 |
| | 889 |
|
Accrued advertising | 363 |
| | 626 |
|
Accrued royalties | 3,001 |
| | 2,868 |
|
Accrued commissions | 677 |
| | 725 |
|
Derivative liability | 49 |
| | — |
|
Other | 2,807 |
| | 2,722 |
|
| $ | 18,426 |
| | $ | 16,608 |
|
NOTE 8—LONG-TERM DEBT
Long-term debt consists of the following (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | |
| June 29,
2013 | | June 30,
2012 |
Revolving U.S. credit facility, interest at base rate or adjusted LIBOR rate plus an applicable margin (interest at 2.6% on June 29, 2013) due May 2016 | $ | 88,753 |
| | $ | 103,965 |
|
Revolving credit facility with Banco Ficohsa, a Honduran bank, interest at 7% due March 2019 (denominated in U.S. dollars) | 5,000 |
| | 5,000 |
|
Term loan with Banco Ficohsa, a Honduran bank, interest at 7%, interest only payments thru March 2012, principal payments began April 2012, payable monthly with a seven-year term (denominated in U.S. dollars) | 4,539 |
| | 5,513 |
|
| 98,292 |
| | 114,478 |
|
Less current installments | (3,529 | ) | | (3,529 | ) |
Long-term debt, excluding current installments | $ | 94,763 |
| | $ | 110,949 |
|
On May 27, 2011, Delta Apparel, Soffe (successor by merger to TCX, LLC), Junkfood, To The Game and Art Gun entered into a Fourth Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement (the “Amended Loan Agreement”) with the financial institutions named in the Amended Loan Agreement as Lenders, Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Administrative Agent, Bank of America, N.A., as Syndication Agent, Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Sole Lead Arranger, and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC and Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, as Joint Bookrunners.
Pursuant to the Amended Loan Agreement, the line of credit is $145 million (subject to borrowing base limitations), and matures on May 26, 2016. Provided that no event of default exists, we have the option to increase the maximum credit available under the facility to $200 million (subject to borrowing base limitations), conditioned upon the Agent's ability to secure additional commitments and customary closing conditions. In fiscal year 2011, we paid $1.4 million in financing costs in conjunction with the Amended Loan Agreement.
The credit facility is secured by a first-priority lien on substantially all of the real and personal property of Delta Apparel, Junkfood, Soffe, To The Game, and Art Gun. All loans bear interest at rates, at the Company's option, based on either (a) an adjusted LIBOR rate plus an applicable margin or (b) a base rate plus an applicable margin, with the base rate equal to the greatest of (i) the federal funds rate plus 0.5%, (ii) the LIBOR rate plus 1.0%, or (iii) the prime rate announced by Wells Fargo, National Association. The facility requires monthly installment payments of approximately $0.2 million in connection with fixed asset amortizations, and these amounts reduce the amount of availability under the facility. Annual facility fees are 0.25% or 0.375% (subject to average excess availability) of the amount by which $145 million exceeds the average daily principal balance of the outstanding loans and letters of credit accommodations. The annual facility fees are charged monthly based on the principal balances during the immediately preceding month.
At June 29, 2013, we had $88.8 million outstanding under our U.S. revolving credit facility at an average interest rate of 2.6%, and had the ability to borrow an additional $42.0 million. Our credit facility includes the financial covenant that if the amount of availability falls below an amount equal to 12.5% of the lesser of the borrowing base or $145 million, our Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio (“FCCR”) (as defined in the Amended Loan Agreement) for the preceding 12 month period must not be less than 1.1 to 1.0. As availability was above the minimum, we were not subject to the FCCR covenant at June 29, 2013. In addition, the credit facility includes customary conditions to funding, representations and warranties, covenants, and events of default. The covenants include, among other things, limitations on asset sales, consolidations, mergers, liens, indebtedness, loans, investments, guaranties, acquisitions, dividends, stock repurchases, and transactions with affiliates.
Proceeds of the loans may be used for permitted acquisitions (as defined in the Amended Loan Agreement), general operating expenses, working capital, other corporate purposes, and to finance credit facility fees and expenses. We are allowed to make cash dividends and stock repurchases if (i) as of the date of the payment or repurchase and after giving effect to the payment or repurchase, we have availability on that date of not less than $15 million and average availability for the 30 day period immediately preceding that date of not less than $15 million; and (ii) the aggregate amount of dividends and stock repurchases after May 27, 2011 does not exceed $19 million plus 50% of our cumulative net income (as defined in the Amended Loan Agreement) from the first day of fiscal year 2012 to the date of determination. At June 29, 2013 and July 30, 2012, there was $11.6 million and $14.8 million, respectively, of retained earnings free of restrictions to make cash dividends or stock repurchases.
The U.S. revolving credit facility contains a subjective acceleration clause and a “springing” lockbox arrangement (as defined in FASB Codification No. 470, Debt ("ASC 470")), whereby remittances from customers will be forwarded to our general bank account and will not reduce the outstanding debt until and unless a specified event or an event of default occurs. Pursuant to ASC 470, we classify borrowings under the facility as long-term debt.
In March 2011, we extinguished our existing debt with Banco Ficohsa, a Honduran bank, and entered into a new credit facility with them. Proceeds from the new loan agreement were used to extinguish the existing loan indebtedness and resulted in no gain or loss being recorded upon extinguishment. The debt facility is secured by a first-priority lien on the assets of our Honduran operations and the loan is not guaranteed by the U.S. entity. The installment loan portion of the agreement carries a fixed interest rate of 7% for a term of seven years and is denominated in U.S. dollars. During the first 12 months of the term, the loan required only monthly interest payments with no principal payments. Beginning in April 2012, ratable monthly principal and interest payments are due through the end of the term. As of June 29, 2013, we had $4.5 million outstanding on this loan. The revolving credit portion of the loan has a 7% fixed interest rate with an ongoing 18-month term (expiring March 2019) and is denominated in U.S. dollars. The revolving credit facility requires minimum payments during each 6 month period of the 18-month term; however, the agreement permits additional drawdowns to the extent payments are made, if certain objective covenants are met. The new revolving Honduran debt, by its nature, is not long-term as it requires scheduled payments each six months. However, as the agreement permits us to re-borrow funds up to the amount repaid, subject to certain objective covenants, and we intend to re-borrow funds, subject to the objective criteria, the amounts have been classified as long-term debt. As of June 29, 2013, we had $5 million outstanding on this loan.
The aggregate maturities of debt at June 29, 2013 are as follows (in thousands):
|
| | | |
Fiscal Year | Amount |
2014 | $ | 3,529 |
|
2015 | 3,529 |
|
2016 | 84,614 |
|
2017 | 973 |
|
2018 | 5,647 |
|
| $ | 98,292 |
|
NOTE 9—INCOME TAXES
The provision for income taxes consists of the following (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended |
| June 29,
2013 | | June 30,
2012 | | July 2,
2011 |
Current: | | | | | |
Federal | $ | 40 |
| | $ | (6,795 | ) | | $ | 3,936 |
|
State | 35 |
| | — |
| | 315 |
|
Foreign | 145 |
| | 157 |
| | 167 |
|
Total current | $ | 220 |
| | $ | (6,638 | ) | | $ | 4,418 |
|
Deferred: | | | | | |
Federal | $ | 499 |
| | $ | (284 | ) | | $ | 562 |
|
State | 3 |
| | (985 | ) | | 373 |
|
Total deferred | 502 |
| | (1,269 | ) | | 935 |
|
Provision for (benefit from) income taxes | $ | 722 |
| | $ | (7,907 | ) | | $ | 5,353 |
|
For financial reporting purposes, income (loss) before provision for (benefit from) income taxes includes the following components (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended |
| June 29,
2013 | | June 30,
2012 | | July 2,
2011 |
United States | $ | 1,468 |
| | $ | (21,660 | ) | | $ | 12,814 |
|
Foreign | 8,438 |
| | 11,306 |
| | 9,866 |
|
| $ | 9,906 |
| | $ | (10,354 | ) | | $ | 22,680 |
|
In fiscal year 2012, we generated federal net operating losses of $20.0 million. These net operating losses were classified in income tax receivable at June 30, 2012 as we fully intended to carry these losses back to prior years where we had the taxable income. When we filed our fiscal year 2012 tax return, we carried back the net operating losses against the taxable income from fiscal years 2011 and 2010. The remaining $0.9 million in net operating loss carryforwards is classified in the income tax receivable at June 29, 2013 as it will be applied against our fiscal year 2013 taxable income.
A reconciliation between actual provision for (benefit from) income taxes and the provision for income taxes computed using the federal statutory income tax rate of 34.0% is as follows (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended |
| June 29,
2013 | | June 30,
2012 | | July 2,
2011 |
Income tax expense at the statutory rate | $ | 3,371 |
| | $ | (3,520 | ) | | $ | 7,712 |
|
State income tax expense, net of federal income tax effect | (11 | ) | | (975 | ) | | 561 |
|
Rate difference and nondeductible items in foreign jurisdictions | (16 | ) | | (47 | ) | | (20 | ) |
Impact of foreign earnings in tax-free zone | (2,754 | ) | | (3,683 | ) | | (3,223 | ) |
Valuation allowance adjustments | 75 |
| | 14 |
| | — |
|
Nondeductible compensation | — |
| | 193 |
| | 157 |
|
Nondeductible amortization and other permanent differences | 100 |
| | 91 |
| | 86 |
|
Other | (43 | ) | | 20 |
| | 80 |
|
Provision for (benefit from) income taxes | $ | 722 |
| | $ | (7,907 | ) | | $ | 5,353 |
|
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effect of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and amounts used for income tax purposes. We have not provided deferred taxes on the $44.1 million of undistributed earnings of our foreign subsidiaries where the earnings are considered to be permanently reinvested. The undistributed earnings would become taxable in the United States if we decided to repatriate earnings for business, tax or foreign exchange reasons. If we made that decision, U.S. income taxes would be provided for net of foreign taxes already paid. The determination of the unrecognized deferred tax liability associated with these unremitted earnings is not practical at this time.
Significant components of our deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | |
| June 29,
2013 | | June 30,
2012 |
Deferred tax assets: | | | |
State net operating loss carryforwards | $ | 1,416 |
| | $ | 1,406 |
|
Charitable donation carryforward | 50 |
| | 373 |
|
Derivative — interest rate contracts | 51 |
| | 81 |
|
Alternative minimum tax credit carryforward | 49 |
| | — |
|
Currently nondeductible accruals | 6,665 |
| | 5,555 |
|
Gross deferred tax assets | 8,231 |
| | 7,415 |
|
Less valuation allowance — state net operating loss | (197 | ) | | (122 | ) |
Net deferred tax assets | 8,034 |
| | 7,293 |
|
| | | |
Deferred tax liabilities: | | | |
Depreciation | (3,164 | ) | | (2,704 | ) |
Goodwill and intangibles | (3,762 | ) | | (3,319 | ) |
Other | (123 | ) | | (109 | ) |
Gross deferred tax liabilities | (7,049 | ) | | (6,132 | ) |
Net deferred tax asset | 985 |
| | 1,161 |
|
Less non-current net deferred tax liabilities | 3,571 |
| | 3,803 |
|
Current deferred tax asset | $ | 4,556 |
| | $ | 4,964 |
|
As of June 29, 2013, and June 30, 2012, we had operating loss carryforwards of approximately $31.6 million and $31.1 million, respectively, for state purposes, resulting in deferred tax assets of $1.4 million and $1.4 million, respectively. These carryforwards expire at various intervals through 2032. Our deferred tax asset related to state net operating loss carryforwards is reduced by a valuation allowance to result in deferred tax assets we consider more likely than not to be realized. There was a $75 thousand net change in the total valuation allowance for the year ended June 29, 2013. The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets depends upon the generation of future taxable income during the periods in which those temporary differences become deductible.
FASB Codification No. 740, Income Taxes (“ASC 740”) requires that a position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return be recognized in the financial statements when it is more likely than not (i.e., a likelihood of more than fifty percent) that the position would be sustained upon examination by tax authorities. A recognized tax position is then measured at the largest amount of benefit that is greater than fifty percent likely of being realized upon ultimate settlement. Upon adoption of ASC 740, we did not have any material unrecognized tax benefits, nor did we have any material unrecognized tax benefits as of June 29, 2013. We recognize accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits as components of our income tax provision. We did not have any interest and penalties accrued related to unrecognized tax benefits as of June 29, 2013.
In the second quarter of fiscal year 2013, the Internal Revenue Service commenced an examination of our U.S. income tax returns for our fiscal year 2010. Upon filing the carryback of our net operating losses from fiscal year 2012 to our fiscal years 2011 and 2010 and receiving a cash refund of the taxes previously paid, the Internal Revenue Service expanded the examination to included our U.S. income tax returns for our 2011 and 2012 fiscal years. This examination is anticipated to be completed during the first half of fiscal year 2014. As of June 29, 2013, the Internal Revenue Service has not proposed any significant adjustments to any tax positions. The tax years 2009 to 2012, according to statute, remain open to examination by the major taxing jurisdictions to which we are subject.
NOTE 10—LEASES
We have several non-cancelable operating leases primarily related to buildings, office equipment and computer systems. Certain land and building leases have renewal options generally for periods ranging from 5 to 10 years.
Future minimum lease payments under non-cancelable operating leases as of June 29, 2013 were as follows (in thousands):
|
| | | |
Fiscal Year | Amount |
2014 | $ | 8,353 |
|
2015 | 7,470 |
|
2016 | 5,180 |
|
2017 | 2,654 |
|
2018 | 294 |
|
Thereafter | — |
|
| $ | 23,951 |
|
Rent expense for all operating leases was $9.8 million, $10.0 million and $9.7 million for fiscal years 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively.
NOTE 11—EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS
We sponsor and maintain a 401(k) retirement savings plan (the “401(k) Plan”) for our employees who meet certain service and age requirements. The 401(k) Plan permits participants to make pre-tax contributions by salary reduction pursuant to Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code. The 401(k) Plan provides for us to make a guaranteed match of the employee’s contributions. We contributed approximately $1.3 million, $1.3 million and $1.2 million to the 401(k) Plan during fiscal years 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively.
We provide post-retirement life insurance benefits for certain retired employees. The plan is noncontributory and is unfunded, and therefore, benefits and expenses are paid from our general assets as they are incurred. All of the employees in the plan are fully vested and the plan was closed to new employees in 1990. The discount rate used in determining the liability was 6.0% for fiscal years 2013 and 2012. The following table presents the benefit obligation for these benefits, which is included in accrued expenses in the accompanying balance sheets (in thousands).
|
| | | | | | | |
| June 29,
2013 | | June 30,
2012 |
Balance at beginning of year | $ | 526 |
| | $ | 580 |
|
Interest expense | 6 |
| | 6 |
|
Benefits paid | (62 | ) | | (61 | ) |
Actuarial adjustment | 1 |
| | 1 |
|
Balance at end of year | $ | 471 |
| | $ | 526 |
|
NOTE 12—STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION
On November 11, 2010, the Delta Apparel, Inc. shareholders approved the Delta Apparel, Inc. 2010 Stock Plan ("2010 Stock Plan"). Upon shareholder approval of the 2010 Stock Plan, no additional awards have been or will be granted under either the Delta Apparel Stock Option Plan ("Option Plan") or the Delta Apparel Incentive Stock Award Plan ("Award Plan"); instead, all stock awards have and will be granted under the 2010 Stock Plan. We account for these plans pursuant to ASC 718, SAB 107 and SAB 110. Shares are generally issued from treasury stock upon exercise of the options or the vesting of the restricted stock units and performance units. ASC 718 requires that cash flows from tax benefits attributable to tax deductions in excess of the compensation cost recognized for those options (excess tax benefits) be classified as financing cash flows. Total stock-based compensation expense was $1.2 million, $1.6 million and $2.1 million in 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively. Associated with the compensation cost are income tax benefits recognized of $0.5 million, $0.6 million and $0.8 million in fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
2010 Stock Plan
Under the 2010 Stock Plan, the Compensation Committee of our Board of Directors has the authority to determine the employees and directors to whom awards may be granted and the size and type of each award and manner in which such awards will vest. The awards available consist of stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, restricted stock units, performance stock, performance units, and cash awards. The aggregate number of shares of common stock that may be delivered under the 2010 Stock Plan is 500,000 plus any shares of common stock subject to outstanding awards under the Option Plan or Award Plan that are subsequently forfeited or terminated for any reason before being exercised. The 2010 Stock Plan limits the number of shares that may be covered by awards to any participant in a given calendar year and also limits the aggregate awards of restricted stock, restricted stock units and performance stock granted in any given calendar year. If a participant dies or becomes disabled (as defined in the 2010 Stock Plan) while employed by or serving as a director, all unvested awards become fully vested. The Compensation Committee is authorized to establish the terms and conditions of awards granted under the 2010 Stock Plan, to establish, amend and rescind any rules and regulations relating to the 2010 Stock Plan, and to make any other determinations that it deems necessary.
Compensation expense is recorded on the cost of sales and selling, general and administrative expense line items in our Statements of Operations over the vesting periods.
Stock Options
Stock options were granted with an average exercise price of $13.47. All outstanding options granted by us have vested and are exercisable.
A summary of the stock option activity during fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011 is presented below:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fiscal Year 2013 | | Fiscal Year 2012 | | Fiscal Year 2011 |
| Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price | | Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price | | Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Stock options outstanding, beginning of fiscal year | 50,000 |
| $ | 13.47 |
| | 50,000 |
| $ | 13.47 |
| | — |
| — |
|
Stock options granted | — |
| — |
| | — |
| — |
| | 50,000 |
| $ | 13.47 |
|
Stock options exercised | — |
| — |
| | — |
| — |
| | — |
| — |
|
Stock options forfeited | — |
| — |
| | — |
| — |
| | — |
| — |
|
Stock options outstanding, end of fiscal year | 50,000 |
| $ | 13.47 |
| | 50,000 |
| $ | 13.47 |
| | 50,000 |
| $ | 13.47 |
|
Stock options outstanding and exercisable, end of fiscal year | 50,000 |
| $ | 13.47 |
| | 50,000 |
| $ | 13.47 |
| | 25,000 |
| $ | 13.47 |
|
The following table summarizes the weighted average grant date fair values and assumptions that were used to estimate the grant date fair values using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model of the options granted during fiscal year 2011:
|
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | 2011 |
Risk-free interest rate | | | | | 2 | % |
Expected life | | | | | 4.0 yrs |
|
Expected volatility | | | | | 63 | % |
Expected dividend yield | | | | | — | % |
Weighted-average per share fair value of options granted | | | | | $ | 6.25 |
|
The risk-free interest rate for the periods within the expected life of the option is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant. Due to minimal exercising of stock options historically, in 2011 we estimated the expected life of options granted to be the midpoint between the average vesting term and the contractual term as permitted under SAB 107 and SAB 110. The expected volatility for the periods of the expected life of the option is determined using historical volatilities based on historical stock prices. The expected dividend yield is based on our expected annual dividend in relation to our historical average stock price.
The aggregate intrinsic value for options outstanding and exercisable as of June 29, 2013 was approximately $1.2 million. The following table summarizes information about our stock options outstanding, all of which are exercisable as of June 29, 2013:
|
| | | | | | | | | |
Date of Option Grant | Number of Options Outstanding and Exercisable | Exercise Price | Grant-Date Fair Value | Expiration Date |
February 2, 2011 | 25,000 |
| $ | 13.86 |
| $ | 6.15 |
| February 18, 2018 |
February 2, 2011 | 25,000 |
| $ | 13.07 |
| $ | 6.35 |
| February 18, 2018 |
| 50,000 |
| | | |
Restricted Stock Units and Performance Units
The following table summarizes the restricted stock units and performance units award activity during fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fiscal Year 2013 | | Fiscal Year 2012 | | Fiscal Year 2011 |
| Number of Units | Weighted average grant date fair value | | Number of Units | Weighted average grant date fair value | | Number of Units | Weighted average grant date fair value |
Units outstanding, beginning of fiscal year | 337,700 |
| $ | 16.05 |
| | — |
| — |
| | — |
| — |
|
Units granted | 10,000 |
| $ | 13.66 |
| | 390,900 |
| $ | 16.04 |
| | — |
| — |
|
Units forfeited | (122,830 | ) | $ | 17.10 |
| | (53,200 | ) | $ | (16.00 | ) | | — |
| — |
|
Units outstanding, end of fiscal year | 224,870 |
| $ | 15.37 |
| | 337,700 |
| $ | 16.05 |
| | — |
| — |
|
During fiscal years 2013 and 2012, restricted stock units representing 5,000 and 91,450 shares of our common stock, respectively, were granted. These restricted stock units are service-based and vest upon the filing of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended June 29, 2013. The restricted stock units are payable in the common stock of Delta Apparel, Inc. and are therefore accounted for under the equity method pursuant to ASC 718.
During fiscal year 2013 and 2012, performance units representing 5,000 and 91,450 shares of our common stock, respectively, were granted. The performance units are based on the achievement of certain performance criteria for the two-year period ended June 29, 2013, payable in the common stock of Delta Apparel, Inc. and vest with the filing of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended June 29, 2013, subject to the achievement of the performance goals. We accounted for these performance units under the equity method pursuant to ASC 718. During the second quarter of fiscal year 2013, we determined that the ability to achieve the performance criteria was not probable. As a result, we reversed the $0.4 million of related share-based expense previously recognized. The performance criteria was not met and the performance units were forfeited on June 29, 2013.
During fiscal year 2012, performance units representing 52,000 shares of our common stock were also granted. These performance units were based on the achievement of certain performance criteria for the fiscal year ended June 30, 2012, and would have vested upon the filing of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for fiscal year 2012; however, the performance criteria was not met and the performance units were forfeited on June 30, 2012.
In addition, during fiscal year 2012, performance units representing 156,000 shares of our common stock were granted. These units are based on the achievement of one-year performance criteria for each of the fiscal years 2013, 2014 and 2015, with one third of such units eligible to vest with the filing of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for each of the fiscal years. Upon achievement of the performance goals, one-half are payable in the common stock of Delta Apparel, Inc. and are therefore accounted for under the equity method pursuant to ASC 718 and one-half are payable in cash and are therefore accounted for under the liability method pursuant to ASC 718. Based upon the performance achieved during fiscal year 2013, 39,520 units of the 52,000 units granted vest upon the filing of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended June 29, 2013 and 12,480 units were forfeited on June 29, 2013.
As of June 29, 2013, there was $1.1 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested restricted stock units and performance units under the 2010 Stock Plan. This cost is expected to be recognized over a period of 2.3 years.
The following table summarizes information about the unvested restricted stock units and performance units as of June 29, 2013.
|
| | | | | | |
Restricted Stock Units/Performance Units | Number of Units | Average Market Price on Date of Grant | Vesting Date |
Fiscal year 2012 Restricted Stock Units | 76,350 |
| $ | 17.60 |
| August 2013 |
Fiscal year 2012 Performance Units | 39,520 |
| $ | 14.25 |
| August 2013 |
Fiscal year 2012 Performance Units | 52,000 |
| $ | 14.25 |
| August 2014 |
Fiscal year 2012 Performance Units | 52,000 |
| $ | 14.25 |
| August 2015 |
Fiscal year 2013 Restricted Stock Units | 5,000 |
| $ | 13.66 |
| August 2013 |
| 224,870 |
| | |
Option Plan
Prior to expiration of the Option Plan, the Compensation Committee of our Board of Directors had the discretion to grant options for up to 2,000,000 shares of common stock to officers and key and middle level executives for the purchase of our stock at prices not less than fifty percent of the fair market value of the shares on the dates of grant, with an exercise term (as determined by the Compensation Committee) not to exceed 10 years. The Compensation Committee determined the vesting period for the stock options, which generally became exercisable over three to four years. Certain option awards in the Option Plan provided for accelerated vesting upon meeting specific retirement, death or disability criteria.
Compensation expense was recorded on the cost of sales and selling, general and administrative expense line items in our Statements of Operations on a straight-line basis over the vesting periods.
A summary of our stock option activity during fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011 is presented below:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fiscal Year 2013 | | Fiscal Year 2012 | | Fiscal Year 2011 |
| Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price | | Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price | | Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Stock options outstanding, beginning of fiscal year | 799,834 |
| $ | 12.22 |
| | 851,167 |
| $ | 12.16 |
| | 1,024,500 |
| 11.89 |
|
Stock options exercised | (139,334 | ) | 11.14 |
| | (25,333 | ) | 8.11 |
| | (118,667 | ) | 11.64 |
|
Stock options forfeited | (60,000 | ) | 15.91 |
| | (26,000 | ) | 14.48 |
| | (54,666 | ) | 8.16 |
|
Stock options outstanding, end of fiscal year | 600,500 |
| $ | 12.09 |
| | 799,834 |
| $ | 12.22 |
| | 851,167 |
| $ | 12.16 |
|
Stock options outstanding and exercisable, end of fiscal year | 600,500 |
| $ | 12.09 |
| | 799,834 |
| $ | 12.22 |
| | 777,168 |
| $ | 12.55 |
|
The total intrinsic value of options exercised during fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011 was $0.7 million, $0.2 million and $0.6 million respectively. During fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011, exercised options resulted in excess tax benefits of $34 thousand, $529 thousand and $84 thousand, respectively. All outstanding options were vested as of June 30, 2012.
The following table summarizes information about our stock options outstanding, all of which are exercisable as of June 29, 2013:
|
| | | | | | | | | |
Date of Option Grant | Number of Options Outstanding and Exercisable | Exercise Price | Grant-Date Fair Value | Expiration Date |
June 28, 2004 | 82,500 |
| $ | 11.28 |
| $ | 4.23 |
| June 28, 2014 |
July 4, 2005 | 358,000 |
| $ | 13.35 |
| $ | 5.18 |
| July 4, 2015 |
July 27, 2006 | 30,000 |
| $ | 17.24 |
| $ | 6.20 |
| July 27, 2016 |
February 8, 2008 | 120,000 |
| $ | 8.30 |
| $ | 2.95 |
| February 8, 2018 |
March 16, 2009 | 10,000 |
| $ | 4.01 |
| $ | 2.00 |
| February 18, 2018 |
| 600,500 |
| | | |
Award Plan
Under the Award Plan, the Compensation Committee of our Board of Directors had the discretion to grant awards for up to an aggregate maximum of 800,000 shares of our common stock. The Award Plan authorized the Compensation Committee to grant to our officers and key and middle level executives rights to acquire shares at a cash purchase price of $0.01 per share. The Award Plan contained provisions for cash payments equal to the taxes due when the shares vest. Therefore, pursuant to ASC 718, the underlying stock grant was accounted for as an equity award and the associated cash payment as a liability award.
In fiscal year 2011, prior to the adoption of the 2010 Stock Plan, awards for up to 7,000 shares of our common stock were granted. The award was comprised of 4,200 shares which were service-based and vested upon the filing on our Annual Report of Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended July 2, 2011. The remaining 2,800 shares were performance awards and were based on the achievement of performance criteria for the two-year period ended July 2, 2011 and vested upon the filing of our Annual Report of Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended July 2, 2011, subject to the performance criteria.
Compensation expense was recorded on the cost of sales and selling, general and administrative expense line items in our Statements of Operations over the vesting period. There were no outstanding awards under the Award Plan as of June 29, 2013.
NOTE 13—BUSINESS SEGMENTS
We operate our business in two distinct segments: branded and basics. Although the two segments are similar in their production processes and regulatory environments, they are distinct in their economic characteristics, products, marketing and distribution methods.
The branded segment is comprised of our business units which are focused on specialized apparel garments and headwear to meet consumer preferences and fashion trends, and includes Soffe, Junkfood, To The Game and Art Gun. These branded embellished and unembellished products are sold through specialty and boutique shops, upscale and traditional department stores, mid-tier retailers, sporting goods stores, college bookstores and the U.S. military. Products in this segment are marketed under our lifestyle brands of
Soffe®, Intensity Athletics®, Junk Food®, The Game®, American Threads™, Salt Life® and Realtree Outfitters® as well as other labels. The results of The Cotton Exchange have been included in the branded segment since its acquisition on July 12, 2010.
The basics segment is comprised of our business units primarily focused on garment styles that are characterized by low fashion risk, and includes our Delta Catalog and FunTees businesses. We market, distribute and manufacture for sale unembellished knit apparel under the main brands of Delta Pro Weight® and Delta Magnum Weight® for sale to a diversified audience ranging from large licensed screen printers to small independent businesses. We also manufacture private label products for major branded sportswear companies, retailers, corporate industry programs, and sports licensed apparel marketers. Typically these products are sold with value-added services such as hangtags, ticketing, hangers, and embellishment so that they are fully ready for retail.
Robert W. Humphreys, our chief operating decision maker, and management evaluate performance and allocate resources based on profit or loss from operations before interest, income taxes and special charges (“segment operating income (loss)”). Our segment operating income (loss) may not be comparable to similarly titled measures used by other companies. The accounting policies of our reportable segments are the same as those described in Note 2. Intercompany transfers between operating segments are transacted at cost and have been eliminated within the segment amounts shown in the following table (in thousands). We expensed a one-time charge of $1.2 million in the fiscal 2013 first quarter for legal and professional fees related to the previously disclosed Audit Committee internal investigation that was completed during that quarter. This one time charge is included in the basics segment.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basics | | Branded | | Consolidated |
Fiscal Year 2013: | | | | | |
Net sales | $ | 270,876 |
| | $ | 219,647 |
| | $ | 490,523 |
|
Segment operating income (loss) | 15,771 |
| | (1,868 | ) | | 13,903 |
|
Segment assets ** | 161,716 |
| | 150,194 |
| | 311,910 |
|
Equity investment in joint venture | 2,909 |
| | — |
| | 2,909 |
|
Purchases of property and equipment | 3,477 |
| | 4,445 |
| | 7,922 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | 5,149 |
| | 2,866 |
| | 8,015 |
|
| | | | | |
Fiscal Year 2012: | | | | | |
Net sales | $ | 254,718 |
| | $ | 235,205 |
| | $ | 489,923 |
|
Segment operating (loss) income | (12,484 | ) | | 6,262 |
| | (6,222 | ) |
Segment assets ** | 168,492 |
| | 151,902 |
| | 320,394 |
|
Equity investment in joint venture | 2,818 |
| | — |
| | 2,818 |
|
Purchases of property and equipment | 3,828 |
| | 2,798 |
| | 6,626 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | 5,547 |
| | 1,945 |
| | 7,492 |
|
| | | | | |
Fiscal Year 2011: | | | | | |
Net sales | $ | 253,494 |
| | $ | 221,742 |
| | $ | 475,236 |
|
Gain on contingent consideration, net of impairment charges * | — |
| | 918 |
| | 918 |
|
Segment operating income | 16,889 |
| | 8,407 |
| | 25,296 |
|
Segment assets ** | 162,932 |
| | 148,933 |
| | 311,865 |
|
Equity investment in joint venture | 2,664 |
| | — |
| | 2,664 |
|
Purchases of property and equipment | 4,164 |
| | 3,802 |
| | 7,966 |
|
Depreciation and amortization | 4,912 |
| | 2,345 |
| | 7,257 |
|
______________________
|
| | |
* | | See Note 2(m) for further information regarding the remeasurement of contingent consideration and impairment testing of goodwill and intangibles. |
|
| | |
** | | All goodwill and intangibles on our balance sheet is included in the branded segment. |
The following reconciles the segment operating income (loss) to the consolidated income (loss) before provision for (benefit from) income taxes (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended |
| June 29,
2013 | | June 30, 2012 |
| | July 2, 2011 |
|
Segment operating income (loss) | $ | 13,903 |
| | $ | (6,222 | ) | | $ | 25,296 |
|
Unallocated interest expense | 3,997 |
| | 4,132 |
| | 2,616 |
|
Consolidated income (loss) before provision for (benefit from) income taxes | $ | 9,906 |
| | $ | (10,354 | ) | | $ | 22,680 |
|
Our revenues include sales to domestic and foreign customers. Foreign customers are composed of companies whose headquarters are located outside of the United States. Supplemental information regarding our revenues by geographic area based on the location of the customer is as follows (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended |
| June 29,
2013 | | June 30, 2012 |
| | July 2, 2011 |
|
United States | $ | 480,981 |
| | $ | 484,419 |
| | $ | 470,909 |
|
Foreign | 9,542 |
| | 5,504 |
| | 4,327 |
|
Total net sales | $ | 490,523 |
| | $ | 489,923 |
| | $ | 475,236 |
|
Our long-lived assets, excluding goodwill and intangible assets, consist of property, plant and equipment for all locations. We attribute our property, plant and equipment to a particular country based on the location of the long-lived assets. Summarized financial information by geographic area is as follows (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | |
| June 29, 2013 | | June 30, 2012 |
United States | $ | 23,011 |
| | $ | 22,146 |
|
| | | |
Honduras | 12,144 |
| | 13,220 |
|
El Salvador | 3,163 |
| | 2,979 |
|
Mexico | 1,128 |
| | 1,080 |
|
All foreign countries | 16,435 |
| | 17,279 |
|
| | | |
Total long-lived assets, excluding goodwill and intangibles | $ | 39,446 |
| | $ | 39,425 |
|
NOTE 14—REPURCHASE OF COMMON STOCK
As of June 30, 2012, our Board of Directors had authorized management to use up to $20.0 million to repurchase stock in open market transactions under our Stock Repurchase Program. On January 23, 2013, the Board of Directors authorized an additional $10.0 million for share repurchases, bringing the aggregate total authorized to $30.0 million.
During fiscal years 2013, 2012 and 2011, we purchased 544,576 shares, 168,120 shares and 176,756 shares, respectively, of our common stock for a total cost of $7.8 million, $2.6 million and $2.5 million, respectively. As of June 29, 2013, we have purchased 1,914,223 shares of common stock for an aggregate of $22.0 million since the inception of the Stock Repurchase Program. All purchases were made at the discretion of management and pursuant to the safe harbor provisions of SEC Rule 10b-18. As of June 29, 2013, $8.0 million remained available for future purchases under our Stock Repurchase Program, which does not have an expiration date.
The following table summarizes the purchases of our common stock for the quarter ended June 29, 2013:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Period | | Total Number of Shares Purchased | | Average Price Paid per Share | | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans | | Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Plans |
March 31 to May 5, 2013 | | 29,470 |
| | $14.41 | | 29,470 |
| |
| $10.8 | million |
May 6 to June 1, 2013 | | 89,582 |
| | $14.05 | | 89,582 |
| |
| $9.6 | million |
June 2 to June 29, 2013 | | 109,302 |
| | $14.73 | | 109,302 |
| |
| $8.0 | million |
Total | | 228,354 |
| | $14.42 | | 228,354 |
| |
| $8.0 | million* |
* As of June 29, 2013
NOTE 15—COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
(a) Litigation
We previously received an inquiry from the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission (“Commission”) regarding a children's drawstring hoodie product sourced, distributed and sold by our Junkfood division and its compliance with applicable product safety standards. The Commission subsequently investigated the matter, including whether Junkfood complied with the reporting requirements of the Consumer Product Safety Act (“CPSA”), and the garments in question were ultimately recalled. On or about July 25, 2012, Junkfood received notification from the Commission staff alleging that Junkfood knowingly violated CPSA Section 15(b) and that it will recommend to the Commission a $900,000 civil penalty. We contend that the Commission's allegations are without merit.
Junkfood has subsequently responded to the Commission staff regarding its recommended penalty, setting forth a number of defenses and mitigating factors that could result in a much lower penalty, if any, ultimately imposed by a court should the matter proceed to litigation. Since then the Commission has requested additional information from Junkfood regarding the matter. While we will continue to defend against these allegations, we believe it is probable that a liability has been incurred. Based upon the terms of previously published CPSC settlements and related product recall notices, we believe if we settle the matter the minimum settlement amount would be $25,000. Should the Commission seek enforcement of the recommended civil penalty and ultimately prevail on its claims at trial, we could be required to pay amounts exceeding $900,000, along with interest and the Commission's costs and fees. During the quarter ended June 30, 2012, we recorded a liability for the most likely outcome within this range and this liability remains recorded as of June 29, 2013.
In addition, at times we are party to various legal claims, actions and complaints. We believe that, as a result of legal defenses, insurance arrangements, and indemnification provisions with parties believed to be financially capable, such actions should not have a material effect on our operations, financial condition, or liquidity.
(b) Purchase Contracts
We have entered into agreements, and have fixed prices, to purchase yarn, natural gas, finished fabric, and finished apparel and headwear products. At June 29, 2013, minimum payments under these contracts were as follows (in thousands):
|
| | | |
Yarn | $ | 14,408 |
|
Natural Gas | 1,507 |
|
Finished fabric | 1,445 |
|
Finished products | 26,256 |
|
| $ | 43,616 |
|
(c) Letters of Credit
As of June 29, 2013, we had outstanding standby letters of credit totaling $0.4 million and outstanding commercial letters of credit totaling $1.0 million.
(d) Derivatives
From time to time we may use interest rate swaps or other instruments to manage our interest rate exposure and reduce the impact of future interest rate changes. These financial instruments are not used for trading or speculative purposes. The following financial instruments were outstanding as of June 29, 2013:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| Effective Date | | Notational Amount | | LIBOR Rate | | Maturity Date |
Interest Rate Swap | 9/1/2011 | | $10 million | | 0.7650 | % | | 9/1/2013 |
Interest Rate Swap | 9/1/2011 | | $10 million | | 0.9025 | % | | 3/1/2014 |
Interest Rate Swap | 9/1/2011 | | $10 million | | 1.0700 | % | | 9/1/2014 |
FASB Codification No. 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (“ASC 820”), defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. Assets and liabilities measured at fair value are grouped in three levels. The levels prioritize the inputs used to measure the fair value of the assets or liabilities. These levels are:
| |
◦ | Level 1 – Quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. |
| |
◦ | Level 2 – Inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for assets and liabilities, either directly or indirectly. These inputs include quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets and quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in market that are less active. |
| |
◦ | Level 3 – Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity for assets or liabilities and includes certain pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies and similar techniques. |
The following financial liabilities are measured at fair value on a recurring basis (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Fair Value Measurements Using |
Period Ended | Total | | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets (Level 1) | | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
Interest Rate Swap | | | | | | | |
June 29, 2013 | $ | 133 |
| | — |
| | $ | 133 |
| | — |
|
June 30, 2012 | $ | 209 |
| | — |
| | $ | 209 |
| | — |
|
July 2, 2011 | $ | 22 |
| | — |
| | $ | 22 |
| | — |
|
| | | | | | | |
Contingent Consideration | | | | | | | |
June 29, 2013 | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
June 30, 2012 | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
July 2, 2011 | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
The fair value of the interest rate swap agreements were derived from discounted cash flow analysis based on the terms of the contract and the forward interest rate curve adjusted for our credit risk, which fall in level 2 of the fair value hierarchy. We used the historical results and projected cash flows based on the contractually defined terms, discounted as necessary, to estimate the fair value of the contingent consideration for Art Gun. Accordingly, the fair value measurement for contingent consideration falls in level 3 of the fair value hierarchy. The contingent consideration for Art Gun is remeasured at the end of each reporting period. Additionally, we remeasured the Art Gun goodwill to fair value in the period ended January 1, 2011. See Note 2(m) - Impairment of Goodwill for further discussion.
The following table summarizes the fair value and presentation in the Consolidated Balance Sheets for derivatives as of June 29, 2013 and June 30, 2012.
|
| | | | | | | |
| June 29,
2013 | | June 30,
2012 |
Accrued expenses | $ | 49 |
| | $ | — |
|
Deferred tax liabilities | (51 | ) | | (80 | ) |
Other liabilities | 84 |
| | 209 |
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | $ | 82 |
| | $ | 129 |
|
(e) License Agreements
We have entered into license agreements that provide for royalty payments of net sales of licensed products as set forth in the agreements. These license agreements are within our branded segment. We have incurred royalty expense (included in selling, general and administrative expenses) of approximately $15.7 million, $15.2 million and $12.4 million during fiscal years 2013, 2012, and 2011, respectively.
At June 29, 2013, based on minimum sales requirements, future minimum royalty payments required under these license agreements were as follows (in thousands):
|
| | | |
Fiscal Year | Amount |
2014 | $ | 3,100 |
|
2015 | 2,204 |
|
2016 | 882 |
|
2017 and thereafter | — |
|
| $ | 6,186 |
|
NOTE 16—QUARTERLY FINANCIAL INFORMATION (UNAUDITED)
Presented below is a summary of our unaudited consolidated quarterly financial information for the fiscal years ended June 29, 2013 and June 30, 2012 (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 Quarter Ended | | 2012 Quarter Ended |
| September 29 | | December 29 | | March 30 | | June 29 | | September 29 | | December 29 | | March 31 | | June 30 |
Net sales | $ | 130,114 |
| | $ | 106,750 |
| | $ | 120,092 |
| | $ | 133,567 |
| | $ | 123,523 |
| | $ | 105,486 |
| | $ | 125,541 |
| | $ | 135,373 |
|
Gross profit | 31,853 |
| | 22,755 |
| | 26,415 |
| | 28,486 |
| | 31,253 |
| | 141 |
| | 25,191 |
| | 27,138 |
|
Operating income (loss) | 5,836 |
| | 846 |
| | 2,564 |
| | 4,657 |
| | 6,698 |
| | (19,989 | ) | | 2,856 |
| | 4,213 |
|
Net earnings (loss) | 3,564 |
| | 46 |
| | 1,608 |
| | 3,966 |
| | 4,412 |
| | (13,592 | ) | | 1,919 |
| | 4,814 |
|
| | |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| | | | | | | | |
Basic EPS | $ | 0.42 |
| | $ | 0.01 |
| | $ | 0.20 |
| | $ | 0.49 |
| | $ | 0.52 |
| | $ | (1.61 | ) | | $ | 0.23 |
| | $ | 0.57 |
|
Diluted EPS | $ | 0.41 |
| | $ | 0.01 |
| | $ | 0.19 |
| | $ | 0.48 |
| | $ | 0.50 |
| | $ | (1.61 | ) | | $ | 0.22 |
| | $ | 0.55 |
|
NOTE 17—SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
Acquisition of Salt Life Assets
On August 27, 2013, To The Game, LLC, our wholly-owned subsidiary, purchased substantially all of the assets of Salt Life Holdings, LLC, including all of its domestic and international trademark rights in the Salt Life brand (the "Salt Life Acquisition"), pursuant to an agreement entered into as of the same date (the "Asset Purchase Agreement"). The Salt Life Acquisition continues our strategy of building lifestyle brands. The purchase price for the Salt Life Transaction consists of $15.0 million in cash, $3.0 million of which was deposited into an escrow account to be held to secure indemnification obligations under the Asset Purchase Agreement, two promissory notes in the aggregate principal amount of $22 million, and a payment contingent on certain performance targets being met with respect to the sale of Salt Life products in calendar 2019. Due to the timing of the acquisition and the issuance of financial statements, management is still in the process of gathering information for the completion of the valuation of the acquired assets for the purchase price allocation and related disclosures. The next quarterly report will have all relevant information. We financed the cash portion of the purchase price through the below-referenced Amended Loan Agreement.
The foregoing summary of the Salt Life Acquisition is qualified in its entirety by reference to the text of the Asset Purchase Agreement, which was filed as Exhibit 2.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed on August 29, 2013.
Amended Loan Agreement
On August 27, 2013, Delta Apparel, To The Game, Junkfood, Soffe, and Art Gun entered into a Consent and First Amendment to the Fourth Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement with Wells Fargo Bank, National Association and the other lenders set forth therein (the “Amended Loan Agreement”). The Fourth Amended and Restated Loan and Security Agreement dated as of May 27, 2011, which was amended by the Amended Loan Agreement, was filed as Exhibit 10.1 to a Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on June 3, 2011.
Pursuant to the Amended Loan Agreement, in general and among other things, (1) the lenders and agent parties consented to the Salt Life Acquisition, (2) the maturity of the loans (other than the FILO Tranche B, as defined below) under the Amended Loan Agreement was extended one year to May 27, 2017, (3) the lenders consented to Delta Apparel's Honduran subsidiaries borrowing up to $10,000,000 from a certain Honduran bank in connection with the purchase of certain equipment, and (4) a first in last out Tranche B (“FILO Tranche B”) was added to provide Delta Apparel and its affiliate parties to the Amended Loan Agreement an additional 5% borrowing availability with respect to eligible accounts receivable and eligible inventory. The FILO Tranche B, and only the FILO Tranche B, will terminate by August 27, 2015 (subject to earlier cancellation by Delta Apparel), has a maximum borrowing amount of $10,000,000, and includes interest rates between 150 and 200 basis points higher than the rates applicable to the other loans available under the Amended Loan Agreement.
The foregoing summary of the Amended Loan Agreement is qualified in its entirety by reference to the text of the Amended Loan Agreement, which was filed as Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed on August 29, 2013.
Change in Fiscal Year End
On August 26, 2013, our Board of Directors determined that the Company's fiscal year will begin on the Sunday closest to September 30th of each year and end on the Saturday closest to September 30th of each year. The change is intended to better align our planning, financial and reporting functions with the seasonality of our business. Under the applicable rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission, we intend to file a transition report on Form 10-QT for the quarter ended September 28, 2013.
Wendell Closing
During the fourth quarter of fiscal year 2013, the decision was made to consolidate our domestic screen print operations, resulting in the closure of the Wendell, North Carolina decorating facility operated by our Soffe business unit and the consolidation of those operations
with Soffe's Fayetteville, North Carolina facility. This closure is expected to take place in September 2013, with associated costs of approximately $1.1 million recorded in the three-month period ending September 28, 2013.
SCHEDULE II — CONSOLIDATED VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
DELTA APPAREL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
(In thousands)
ALLOWANCE FOR DOUBTFUL ACCOUNTS
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Beginning Balance | | Acquisition Accounting * | | Expense | | Write-Offs/ Credits Issued | | Ending Balance |
2013 | $ | 750 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 62 |
| | $ | (156 | ) | | $ | 656 |
|
2012 | 658 |
| | — |
| | 280 |
| | (188 | ) | | 750 |
|
2011 | 761 |
| | — |
| | 711 |
| | (814 | ) | | 658 |
|
RETURNS AND ALLOWANCES |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Beginning Balance | | Acquisition Accounting * | | Expense | | Write-Offs/ Credits Issued | | Ending Balance |
2013 | $ | 1,562 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 8,154 |
| | $ | (8,573 | ) | | $ | 1,143 |
|
2012 | 1,124 |
| | — |
| | 9,864 |
| | (9,426 | ) | | 1,562 |
|
2011 | 1,375 |
| | — |
| | 8,205 |
| | (8,456 | ) | | 1,124 |
|
TOTAL RESERVES FOR ALLOWANCES |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Beginning Balance | | Acquisition Accounting * | | Expense | | Write-Offs/ Credits Issued | | Ending Balance |
2013 | $ | 2,312 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 8,216 |
| | $ | (8,729 | ) | | $ | 1,799 |
|
2012 | 1,782 |
| | — |
| | 10,144 |
| | (9,614 | ) | | 2,312 |
|
2011 | 2,136 |
| | — |
| | 8,916 |
| | (9,270 | ) | | 1,782 |
|
MARKET AND OBSOLESCENCE RESERVE
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Beginning Balance | | Acquisition Accounting * | | Expense ** | | Deductions ** | | Ending Balance |
2013 | $ | 5,151 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 1,616 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 6,767 |
|
2012 | 3,717 |
| | — |
| | 1,434 |
| | — |
| | 5,151 |
|
2011 | 3,782 |
| | — |
| | (65 | ) | | — |
| | 3,717 |
|
SELF INSURANCE RESERVE
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Beginning Balance | | Acquisition Accounting * | | Expense ** | | Deductions ** | | Ending Balance |
2013 | $ | 655 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | (160 | ) | | $ | — |
| | $ | 495 |
|
2012 | 589 |
| | — |
| | 66 |
| | — |
| | 655 |
|
2011 | 777 |
| | 39 |
| | (227 | ) | | — |
| | 589 |
|
DEFERRED TAX ASSET VALUATION ALLOWANCE
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Beginning Balance | | Acquisition Accounting * | | Expense ** | | Deductions ** | | Ending Balance |
2013 | $ | 122 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 75 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 197 |
|
2012 | 108 |
| | — |
| | 14 |
| | — |
| | 122 |
|
2011 | 108 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 108 |
|
______________________
|
| | |
* | | Represents the reserves provided for as a result of the acquisition of The Cotton Exchange. |
|
| | |
** | | Net change in the reserves and allowance are shown in the expense column. |